Worldwide variations in artificial skyglow
- PMID: 25673335
- PMCID: PMC5389131
- DOI: 10.1038/srep08409
Worldwide variations in artificial skyglow
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Worldwide variations in artificial skyglow.Sci Rep. 2015 Aug 5;5:12180. doi: 10.1038/srep12180. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26244555 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
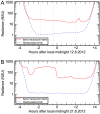
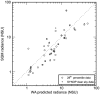
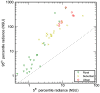
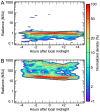
Despite constituting a widespread and significant environmental change, understanding of artificial nighttime skyglow is extremely limited. Until now, published monitoring studies have been local or regional in scope, and typically of short duration. In this first major international compilation of monitoring data we answer several key questions about skyglow properties. Skyglow is observed to vary over four orders of magnitude, a range hundreds of times larger than was the case before artificial light. Nearly all of the study sites were polluted by artificial light. A non-linear relationship is observed between the sky brightness on clear and overcast nights, with a change in behavior near the rural to urban landuse transition. Overcast skies ranged from a third darker to almost 18 times brighter than clear. Clear sky radiances estimated by the World Atlas of Artificial Night Sky Brightness were found to be overestimated by ~25%; our dataset will play an important role in the calibration and ground truthing of future skyglow models. Most of the brightly lit sites darkened as the night progressed, typically by ~5% per hour. The great variation in skyglow radiance observed from site-to-site and with changing meteorological conditions underlines the need for a long-term international monitoring program.
Conflict of interest statement
A.T. is the president of Unihedron, the company that produces the SQM.
Figures

References
-
- Central Intelligence Agency. The World Factbook. URL: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2085.... (2013). Access date 25 August, 2014.
-
- Longcore T. & Rich C. Ecological light pollution. Front Ecol Environ 2, 191–198 (2004).
-
- Rich, C. & Longcore, T. (eds.) Ecological Consequences of Artificial Night Lighting (Island Press, Washington, D.C., USA, 2006).
-
- Hölker F., Wolter C., Perkin E. K. & Tockner K. Light pollution as a biodiversity threat. Trends Ecol Evol 25, 681–682 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Perkin E. et al. The influence of artificial light on freshwater and riparian ecosystems: Questions, challenges, and perspectives. Ecosphere 2, art122 (2011).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

