Coronal diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the kidney: agreement with axial diffusion-weighted magnetic imaging in terms of apparent diffusion coefficient values
- PMID: 25673453
- PMCID: PMC4836254
- DOI: 10.4103/0366-6999.151103
Coronal diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the kidney: agreement with axial diffusion-weighted magnetic imaging in terms of apparent diffusion coefficient values
Abstract
Background: Coronal diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW-MRI) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values have gradually become applied (following conventional axial DW-MRI) in the renal analysis. To explore whether data obtained using coronal DW-MRI are comparable with those derived using axial DW-MRI, this preliminary study sought to assess the agreement in renal ADC values between coronal DW-MRI and axial DW-MRI.
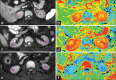
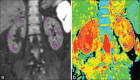
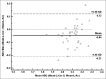
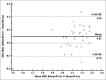
Methods: Thirty-four healthy volunteers were enrolled in the study; written consents were obtained. All subjects underwent respiratory-triggered axial and coronal DW-MRI using a 1.5-MR system with b values of 0 and 800 s/mm 2 . The signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) of the two DW-MRI sequences were measured and statistically compared using the paired t-test. The extent of agreement of ADC values of the upper pole, mid-pole, and lower pole of the kidney; the mean ADC values of the left kidney and right kidney; and the mean ADC values of the bilateral kidneys were evaluated via calculation of intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) or Bland-Altman method between the two DW-MRI sequences.
Results: The SNR of coronal DW-MR images was statistically inferior to that of axial DW-MR images (P < 0.001). The ICCs of the ADC values of each region of interest, and the mean ADC values of bilateral kidneys, between the two sequences, were greater than 0.5, and the mean ADCs of the bilateral kidneys demonstrated the highest ICC (0.869; 95% confidence interval: 0.739-0.935). In addition, 94.1% (32/34), 94.1% (32/34), and 97.1% (31/34) of the ADC bias was inside the limits of agreement in terms of the mean ADC values of the left kidneys, right kidneys, and bilateral kidneys when coronal and axial DWI-MRI were compared.
Conclusions: ADC values derived using coronal DW-MRI exhibited moderate-to-good agreement to those of axial DW-MRI, rendering the former an additional useful DW-MRI method, and causing the ADC values derived using the two types of DW-MRI to be comparable.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Malignant hepatic tumors: short-term reproducibility of apparent diffusion coefficients with breath-hold and respiratory-triggered diffusion-weighted MR imaging.Radiology. 2010 Jun;255(3):815-23. doi: 10.1148/radiol.10091706. Radiology. 2010. PMID: 20501719
-
Diffusion-weighted MRI of the kidneys in patients with familial Mediterranean fever: initial experience.Diagn Interv Radiol. 2009 Dec;15(4):252-5. doi: 10.4261/1305-3825.DIR.2252-08.2. Epub 2009 Oct 5. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2009. PMID: 19813167
-
Functional evaluation of transplanted kidneys with diffusion-weighted and BOLD MR imaging: initial experience.Radiology. 2006 Dec;241(3):812-21. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2413060103. Radiology. 2006. PMID: 17114628
-
Magnetic resonance diffusion-weighted imaging: extraneurological applications.Radiol Med. 2006 Apr;111(3):392-419. doi: 10.1007/s11547-006-0037-0. Epub 2006 Apr 11. Radiol Med. 2006. PMID: 16683086 Review. English, Italian.
-
DW-MRI of the urogenital tract: applications in oncology.Cancer Imaging. 2010 Oct 4;10 Spec no A(1A):S112-23. doi: 10.1102/1470-7330.2010.9030. Cancer Imaging. 2010. PMID: 20880781 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Renal Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Healthy Dogs: Reproducibility, Test-Retest Repeatability, and Selection of the Optimal b-value Combination.Front Vet Sci. 2021 Jul 2;8:641971. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.641971. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 34277748 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the clinical utility of single-shot, readout-segmented and zoomit echo-planar imaging in diffusion-weighted imaging of the kidney at 3 T.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 20;12(1):12389. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16670-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35859112 Free PMC article.
-
How reliable are ADC measurements? A phantom and clinical study of cervical lymph nodes.Eur Radiol. 2018 Aug;28(8):3362-3371. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-5265-2. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Eur Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29476218 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taouli B, Koh DM. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the liver. Radiology. 2010;254:47–66. - PubMed
-
- Wang H, Zhang X, Ye H. Applications of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in renal cell carcinoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2011;11:1017–22. - PubMed
-
- Lassel EA, Rao R, Schwenke C, Schoenberg SO, Michaely HJ. Diffusion-weighted imaging of focal renal lesions: A meta-analysis. Eur Radiol. 2014;24:241–9. - PubMed
-
- Ramírez-Galván YA, Cardona-Huerta S, Ibarra-Fombona E, Elizondo-Riojas G. Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value to evaluate BI-RADS 4 breast lesions: Correlation with pathological findings. Clin Imaging. 2015;39:51–5. - PubMed
-
- Kang TW, Kim SH, Jang KM, Choi D, Ha SY, Kim KM, et al. Gastrointestinal stromal tumours: Correlation of modified NIH risk stratification with diffusion-weighted MR imaging as an imaging biomarker. Eur J Radiol. 2015;84:33–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

