Mercury Reduces the Enzymatic Activity of Neprilysin in Differentiated SH-SY5Y Cells
- PMID: 25673500
- PMCID: PMC4833038
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfv037
Mercury Reduces the Enzymatic Activity of Neprilysin in Differentiated SH-SY5Y Cells
Abstract
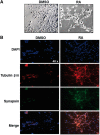
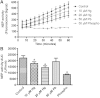
Levels of amyloid beta (Aβ) in the central nervous system are regulated by the balance between its synthesis and degradation. Neprilysin (NEP) is associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD) by its ability to degrade Aβ. Some studies have involved the exposure to mercury (Hg) in AD pathogenesis; therefore, our aim was to investigate the effects on the anabolism and catabolism of Aβ in differentiated SH-SY5Y cells incubated with 1-20 μM of Hg. Exposure to 20 µM of Hg induced an increase in Aβ-42 secretion, but did not increase the expression of the amyloid precursor protein (APP). Hg incubation (10 and 20 µM) increased NEP protein levels; however, it did not change NEP mRNA levels nor the levels of the amyloid intracellular domain peptide, a protein fragment with transcriptional activity. Interestingly, Hg reduced NEP activity at 10 and 20 µM, and circular dichroism analysis using human recombinant NEP showed conformational changes after incubation with molar equivalents of Hg. This suggests that the Hg-induced inhibition of NEP activity may be mediated by a conformational change resulting in reduced Aβ-42 degradation. Finally, the comparative effects of lead (Pb, 50 μM) were evaluated. We found a significant increase in Aβ-42 levels and a dramatic increase in APP protein levels; however, no alteration in NEP levels was observed nor in the enzymatic activity of this metalloprotease, despite the fact that Pb slightly modified the rhNEP conformation. Overall, our data suggest that Hg and Pb increase Aβ levels by different mechanisms.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; amyloid precursor protein; beta-amyloid peptide; lead; mercury; neprilysin; retinoic acid.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society of Toxicology. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures






Similar articles
-
In vitro Pb exposure disturbs the balance between Aβ production and elimination: the role of AβPP and neprilysin.Neurotoxicology. 2011 Jun;32(3):300-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2011.02.001. Epub 2011 Feb 18. Neurotoxicology. 2011. PMID: 21315759 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of HNE-modification induced by Abeta on neprilysin expression and activity in SH-SY5Y cells.J Neurochem. 2009 Feb;108(4):1072-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05855.x. J Neurochem. 2009. PMID: 19196432 Free PMC article.
-
Messenger RNA-based therapeutics for brain diseases: An animal study for augmenting clearance of beta-amyloid by intracerebral administration of neprilysin mRNA loaded in polyplex nanomicelles.J Control Release. 2016 Aug 10;235:268-275. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.06.001. Epub 2016 Jun 6. J Control Release. 2016. PMID: 27282413
-
Neprilysin and Aβ Clearance: Impact of the APP Intracellular Domain in NEP Regulation and Implications in Alzheimer's Disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2013 Dec 23;5:98. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2013.00098. Front Aging Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24391587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NEP-like endopeptidases and Alzheimer's disease [corrected].Curr Alzheimer Res. 2010 May;7(3):223-9. doi: 10.2174/156720510791050849. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2010. PMID: 20088804 Review.
Cited by
-
Biometal Dyshomeostasis and Toxic Metal Accumulations in the Development of Alzheimer's Disease.Front Mol Neurosci. 2017 Oct 24;10:339. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00339. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29114205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Phenolic Components of Gastrodia elata improve Prognosis in Rats after Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion by Enhancing the Endogenous Antioxidant Mechanisms.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Mar 22;2018:7642158. doi: 10.1155/2018/7642158. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 29765502 Free PMC article.
-
Mercury and Alzheimer's disease: a look at the links and evidence.Metab Brain Dis. 2021 Mar;36(3):361-374. doi: 10.1007/s11011-020-00649-5. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Metab Brain Dis. 2021. PMID: 33411216 Review.
-
Dopamine D1-Like Receptor Stimulation Induces CREB, Arc, and BDNF Dynamic Changes in Differentiated SH-SY5Y Cells.Neurochem Res. 2024 Nov 27;50(1):35. doi: 10.1007/s11064-024-04293-8. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 39601897 Free PMC article.
-
The Function of the Metals in Regulating Epigenetics During Parkinson's Disease.Front Genet. 2021 Feb 2;11:616083. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.616083. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33603768 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alattia J. R., Kuraishi T., Dimitrov M., Chang I., Lemaitre B., Fraering P. C. (2011). Mercury is a direct and potent gamma-secretase inhibitor affecting Notch processing and development in Drosophila. FASEB J. 25, 2287–2295. - PubMed
-
- Arima J., Uesugi Y., Hatanaka T. (2009). Bacillus d-stereospecific metallo-amidohydrolase: active-site metal-ion substitution changes substrate specificity. Biochimie 91, 568–576. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong R. A. (1994). Differences in beta-amyloid (beta/A4) deposition in human patients with Down's syndrome and sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci. Lett. 169, 133–136. - PubMed
-
- Atwood C. S., Moir R. D., Huang X., Scarpa R. C., Bacarra N. M., Romano D. M., Hartshorn M. A., Tanzi R. E., Bush A. I. (1998). Dramatic aggregation of Alzheimer abeta by Cu(II) is induced by conditions representing physiological acidosis. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 12817–12826. - PubMed
-
- Beckman M., Iverfeldt K. (1997). Increased gene expression of beta-amyloid precursor protein and its homologues APLP1 and APLP2 in human neuroblastoma cells in response to retinoic acid. Neurosci. Lett. 221, 73–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

