Regulation of luteinizing hormone receptor expression by an RNA binding protein: role of ERK signaling
- PMID: 25673531
- PMCID: PMC4345741
Regulation of luteinizing hormone receptor expression by an RNA binding protein: role of ERK signaling
Abstract
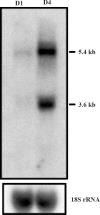
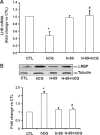
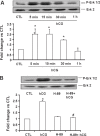
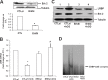
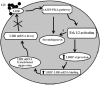
A specific luteinizing hormone receptor (LHR) mRNA binding protein (LRBP) has been identified and purified. This LH receptor mRNA binding protein selectively binds to the polypyrimidine rich bipartite sequence in the coding region of the LHR mRNA and accelerates its degradation. In response to preovulatory LH surge, the LH receptor expression in the ovary undergoes downregulation by accelerated degradation of LH receptor mRNA through the involvement of this RNA binding protein. Here we describe the intracellular mechanism triggered by LH/hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) that leads to the regulated degradation of LH receptor mRNA. Downregulation of LH receptor mRNA was induced by treatment of cultured human granulosa cells with 10 IU of hCG. Activation of downstream target, extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase 1 and 2 (ERK 1/2) showed an increase within five min and sustained up to 1 h. Confocal analysis showed that ERK1/2 translocates to the nucleus after 15 min of hCG treatment. This leads to an increase in LRBP expression which then causes downregulation of LH receptor mRNA by accelerating its degradation. Treatment with UO126 or transfection with ERK specific siRNA (small interfering RNA) resulted in the abolishment of ERK activation as well as LHR mRNA downregulation. RNA electrophoretic mobility gel shift assay of the cytosolic fractions showed that hCG-induced increase in the LH receptor mRNA binding activity was also abrogated by these treatments. These results show that LH/hCG-induced LH receptor mRNA downregulation is initiated by the activation of ERK1/2 pathway by regulating the expression and activity of LH receptor mRNA binding activity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Luteinizing hormone receptor mRNA down-regulation is mediated through ERK-dependent induction of RNA binding protein.Mol Endocrinol. 2011 Feb;25(2):282-90. doi: 10.1210/me.2010-0366. Epub 2010 Dec 8. Mol Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21147848 Free PMC article.
-
miR-122 Regulates LH Receptor Expression by Activating Sterol Response Element Binding Protein in Rat Ovaries.Endocrinology. 2015 Sep;156(9):3370-80. doi: 10.1210/en.2015-1121. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Endocrinology. 2015. PMID: 26125464 Free PMC article.
-
Ribonucleic acid binding protein-mediated regulation of luteinizing hormone receptor expression in granulosa cells: relationship to sterol metabolism.Mol Endocrinol. 2007 Sep;21(9):2233-41. doi: 10.1210/me.2007-0102. Epub 2007 Jun 5. Mol Endocrinol. 2007. PMID: 17550979
-
Regulation of Luteinizing Hormone Receptor mRNA Expression in the Ovary: The Role of miR-122.Vitam Horm. 2018;107:67-87. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2018.01.010. Epub 2018 Feb 19. Vitam Horm. 2018. PMID: 29544643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular regulation of gonadotropin receptor expression: relationship to sterol metabolism.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010 Nov 25;329(1-2):26-32. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2010.05.014. Epub 2010 Jun 4. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 20570710 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Morphology in the Genotype and Phenotype Correlation of Bilateral Macronodular Adrenocortical Disease (BMAD): A Series of Clinicopathologically Well-Characterized 35 Cases.Endocr Pathol. 2023 Jun;34(2):179-199. doi: 10.1007/s12022-023-09751-7. Epub 2023 Mar 2. Endocr Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36864263
-
Sp1 regulates steroidogenic genes and LHCGR expression in primary human luteinized granulosa cells.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2019 Jun;190:183-192. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.04.003. Epub 2019 Apr 4. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30954507 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the gonadotropin receptors during follicular development.Reprod Med Biol. 2017 Dec 7;17(1):11-19. doi: 10.1002/rmb2.12075. eCollection 2018 Jan. Reprod Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29371816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of High-Fructose Diet-Induced Metabolic Syndrome on the Pituitary-Gonadal Axis in Male Rats.Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 23;10(12):3009. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10123009. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36551765 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of RNA structure on ZFP36L2 interaction with luteinizing hormone receptor mRNA.RNA. 2017 Aug;23(8):1209-1223. doi: 10.1261/rna.060467.116. Epub 2017 Apr 28. RNA. 2017. PMID: 28455422 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ascoli M, Fanelli F, Segaloff DL. The lutropin/choriogonadotropin receptor, a 2002 perspective. Endocr Rev. 2002;23:141–74. - PubMed
-
- Rao CV. An overview of the past, present, and future of nongonadal LH/hCG actions in reproductive biology and medicine. Semin Reprod Med. 2001;19:7–17. - PubMed
-
- McFarland KC, Sprengel R, Phillips HS, Kohler M, Rosemblit N, Nikolics K, et al. Lutropin-choriogonadotropin receptor: an unusual member of the G protein-coupled receptor family. Science. 1989;245:494–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
