Thiosulfate dehydrogenase (TsdA) from Allochromatium vinosum: structural and functional insights into thiosulfate oxidation
- PMID: 25673691
- PMCID: PMC4423707
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.623397
Thiosulfate dehydrogenase (TsdA) from Allochromatium vinosum: structural and functional insights into thiosulfate oxidation
Abstract
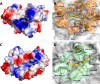
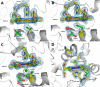
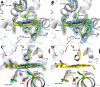
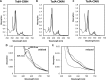
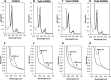
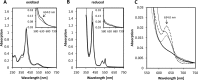
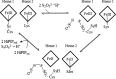
Although the oxidative condensation of two thiosulfate anions to tetrathionate constitutes a well documented and significant part of the natural sulfur cycle, little is known about the enzymes catalyzing this reaction. In the purple sulfur bacterium Allochromatium vinosum, the reaction is catalyzed by the periplasmic diheme c-type cytochrome thiosulfate dehydrogenase (TsdA). Here, we report the crystal structure of the "as isolated" form of A. vinosum TsdA to 1.98 Å resolution and those of several redox states of the enzyme to different resolutions. The protein contains two typical class I c-type cytochrome domains wrapped around two hemes axially coordinated by His(53)/Cys(96) and His(164)/Lys(208). These domains are very similar, suggesting a gene duplication event during evolution. A ligand switch from Lys(208) to Met(209) is observed upon reduction of the enzyme. Cys(96) is an essential residue for catalysis, with the specific activity of the enzyme being completely abolished in several TsdA-Cys(96) variants. TsdA-K208N, K208G, and M209G variants were catalytically active in thiosulfate oxidation as well as in tetrathionate reduction, pointing to heme 2 as the electron exit point. In this study, we provide spectroscopic and structural evidence that the TsdA reaction cycle involves the transient presence of heme 1 in the high-spin state caused by movement of the Sγ atom of Cys(96) out of the iron coordination sphere. Based on the presented data, we draw important conclusions about the enzyme and propose a possible reaction mechanism for TsdA.
Keywords: Allochromatium vinosum; Crystal Structure; Cytochrome c; Enzyme Kinetics; Enzyme Mechanism; Enzyme Mutation; Sulfur; Tetrathionate; Thiosulfate Dehydrogenase; TsdA.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

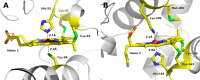
References
-
- Denkmann K., Grein F., Zigann R., Siemen A., Bergmann J., van Helmont S., Nicolai A., Pereira I. A. C., Dahl C. (2012) Thiosulfate dehydrogenase: a wide-spread unusual acidophilic c-type cytochrome. Environ. Microbiol. 14, 2673–2688 - PubMed
-
- Liu Y.-W., Denkmann K., Kosciow K., Dahl C., Kelly D. J. (2013) Tetrathionate stimulated growth of Campylobacter jejuni identifies TsdA as a new type of bi-functional tetrathionate reductase that is widely distributed in bacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 88, 173–188 - PubMed
-
- Imhoff J. F., Süling J., Petri R. (1998) Phylogenetic relationships among the Chromatiaceae, their taxonomic reclassification and description of the new genera Allochromatium, Halochromatium, Isochromatium, Marichromatium, Thiococcus, Thiohalocapsa, and Thermochromatium. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 48, 1129–1143 - PubMed
-
- Hensen D., Sperling D., Trüper H. G., Brune D. C., Dahl C. (2006) Thiosulphate oxidation in the phototrophic sulphur bacterium Allochromatium vinosum. Mol. Microbiol. 62, 794–810 - PubMed
-
- Friedrich C. G., Bardischewsky F., Rother D., Quentmeier A., Fischer J. (2005) Prokaryotic sulfur oxidation. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 8, 253–259 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

