Cytosolic chaperones mediate quality control of higher-order septin assembly in budding yeast
- PMID: 25673805
- PMCID: PMC4454179
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E14-11-1531
Cytosolic chaperones mediate quality control of higher-order septin assembly in budding yeast
Abstract
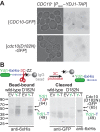
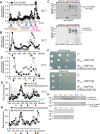
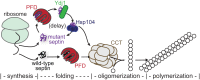
Septin hetero-oligomers polymerize into cytoskeletal filaments with essential functions in many eukaryotic cell types. Mutations within the oligomerization interface that encompasses the GTP-binding pocket of a septin (its "G interface") cause thermoinstability of yeast septin hetero-oligomer assembly, and human disease. When coexpressed with its wild-type counterpart, a G interface mutant is excluded from septin filaments, even at moderate temperatures. We show that this quality control mechanism is specific to G interface mutants, operates during de novo septin hetero-oligomer assembly, and requires specific cytosolic chaperones. Chaperone overexpression lowers the temperature permissive for proliferation of cells expressing a G interface mutant as the sole source of a given septin. Mutations that perturb the septin G interface retard release from these chaperones, imposing a kinetic delay on the availability of nascent septin molecules for higher-order assembly. Un-expectedly, the disaggregase Hsp104 contributes to this delay in a manner that does not require its "unfoldase" activity, indicating a latent "holdase" activity toward mutant septins. These findings provide new roles for chaperone-mediated kinetic partitioning of non-native proteins and may help explain the etiology of septin-linked human diseases.
© 2015 Johnson et al. This article is distributed by The American Society for Cell Biology under license from the author(s). Two months after publication it is available to the public under an Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike 3.0 Unported Creative Commons License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0).
Figures



Similar articles
-
Kinetic partitioning during de novo septin filament assembly creates a critical G1 "window of opportunity" for mutant septin function.Cell Cycle. 2016 Sep 16;15(18):2441-53. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1196304. Epub 2016 Jul 11. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 27398993 Free PMC article.
-
Higher-order septin assembly is driven by GTP-promoted conformational changes: evidence from unbiased mutational analysis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2014 Mar;196(3):711-27. doi: 10.1534/genetics.114.161182. Epub 2014 Jan 7. Genetics. 2014. PMID: 24398420 Free PMC article.
-
Guanidine hydrochloride reactivates an ancient septin hetero-oligomer assembly pathway in budding yeast.Elife. 2020 Jan 28;9:e54355. doi: 10.7554/eLife.54355. Elife. 2020. PMID: 31990274 Free PMC article.
-
Architecture, remodeling, and functions of the septin cytoskeleton.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2019 Jan;76(1):7-14. doi: 10.1002/cm.21475. Epub 2018 Aug 2. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2019. PMID: 29979831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reuse, replace, recycle. Specificity in subunit inheritance and assembly of higher-order septin structures during mitotic and meiotic division in budding yeast.Cell Cycle. 2009 Jan 15;8(2):195-203. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.2.7381. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19164941 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Carboxy-Terminal Tails of Septins Cdc11 and Shs1 Recruit Myosin-II Binding Factor Bni5 to the Bud Neck in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2015 Jul;200(3):843-62. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.176503. Epub 2015 May 12. Genetics. 2015. PMID: 25971666 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetic partitioning during de novo septin filament assembly creates a critical G1 "window of opportunity" for mutant septin function.Cell Cycle. 2016 Sep 16;15(18):2441-53. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1196304. Epub 2016 Jul 11. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 27398993 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical rescue of mutant proteins in living Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells by naturally occurring small molecules.G3 (Bethesda). 2021 Sep 6;11(9):jkab252. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab252. G3 (Bethesda). 2021. PMID: 34544143 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay of septin amphipathic helices in sensing membrane-curvature and filament bundling.Mol Biol Cell. 2021 Oct 1;32(20):br5. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E20-05-0303. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Mol Biol Cell. 2021. PMID: 34319771 Free PMC article.
-
GTPase domain driven dimerization of SEPT7 is dispensable for the critical role of septins in fibroblast cytokinesis.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 28;6:20007. doi: 10.1038/srep20007. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26818767 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alpers JB, Paulus H. Allosteric preconditioning: role of allosteric ligands in promoting the maturation of enzymes. Nature. 1971;233:478–480. - PubMed
-
- Amberg D, Burke D, Strathern J. Methods in Yeast Genetics, Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2005.
-
- Betting J, Seufert W. A yeast Ubc9 mutant protein with temperature-sensitive in vivo function is subject to conditional proteolysis by a ubiquitin- and proteasome-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:25790–25796. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

