Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitors Induce Rapid Overactivation of the MEK/ERK Pathway in Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells through Suppression of mTORC2
- PMID: 25673820
- PMCID: PMC4394038
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0669
Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitors Induce Rapid Overactivation of the MEK/ERK Pathway in Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells through Suppression of mTORC2
Abstract
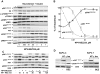
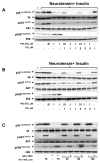
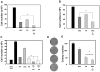
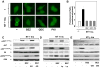
The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, which is aberrantly stimulated in many cancer cells, has emerged as a target for therapy. However, mTORC1/S6K also mediates negative feedback loops that attenuate upstream signaling. Suppression of these feedback loops opposes the growth-suppressive effects of mTOR inhibitors and leads to drug resistance. Here, we demonstrate that treatment of PANC-1 or MiaPaCa-2 pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cells with the dual PI3K/mTOR kinase inhibitor (PI3K/TOR-KI) BEZ235 blocked mTORC1/S6K activation (scored by S6 phosphorylation at Ser(240/244)), mTORC1/4E-BP1 (assayed by 4E-BP1 phosphorylation at Thr(37/46)), and mTORC2-mediated AKT phosphorylation at Ser(473), in a concentration-dependent manner. Strikingly, BEZ235 markedly enhanced the MEK/ERK pathway in a dose-dependent manner. Maximal ERK overactivation coincided with complete inhibition of phosphorylation of AKT and 4E-BP1. ERK overactivation was induced by other PI3K/TOR-KIs, including PKI-587 and GDC-0980. The MEK inhibitors U126 or PD0325901 prevented ERK overactivation induced by PI3K/TOR-KIs. The combination of BEZ235 and PD0325901 caused a more pronounced inhibition of cell growth than that produced by each inhibitor individually. Mechanistic studies assessing PI3K activity in single PDAC cells indicate that PI3K/TOR-KIs act through a PI3K-independent pathway. Doses of PI3K/TOR-KIs that enhanced MEK/ERK activation coincided with those that inhibited mTORC2-mediated AKT phosphorylation on Ser(473), suggesting a role of mTORC2. Knockdown of RICTOR via transfection of siRNA markedly attenuated the enhancing effect of BEZ235 on ERK phosphorylation. We propose that dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors suppress a novel negative feedback loop mediated by mTORC2, thereby leading to enhanced MEK/ERK pathway activity in pancreatic cancer cells.
©2015 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dual inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway suppresses the growth of leiomyosarcomas but leads to ERK activation through mTORC2: biological and clinical implications.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 31;8(5):7878-7890. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13987. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28002802 Free PMC article.
-
Different patterns of Akt and ERK feedback activation in response to rapamycin, active-site mTOR inhibitors and metformin in pancreatic cancer cells.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57289. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057289. Epub 2013 Feb 21. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23437362 Free PMC article.
-
Activity of the novel dual phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 against osteosarcoma.Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(4):602-9. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2015.1017155. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25869769 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse signaling mechanisms of mTOR complexes: mTORC1 and mTORC2 in forming a formidable relationship.Adv Biol Regul. 2019 May;72:51-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2019.03.003. Epub 2019 Apr 11. Adv Biol Regul. 2019. PMID: 31010692 Review.
-
Disentangling the signaling pathways of mTOR complexes, mTORC1 and mTORC2, as a therapeutic target in glioblastoma.Adv Biol Regul. 2022 Jan;83:100854. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2021.100854. Epub 2021 Dec 6. Adv Biol Regul. 2022. PMID: 34996736 Review.
Cited by
-
RAS Function in cancer cells: translating membrane biology and biochemistry into new therapeutics.Biochem J. 2020 Aug 14;477(15):2893-2919. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20190839. Biochem J. 2020. PMID: 32797215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overcoming Adaptive Resistance to KRAS and MEK Inhibitors by Co-targeting mTORC1/2 Complexes in Pancreatic Cancer.Cell Rep Med. 2020 Nov 17;1(8):100131. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100131. eCollection 2020 Nov 17. Cell Rep Med. 2020. PMID: 33294856 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Inhibition of PI3K/Akt and mTOR by the Dietary Antioxidant, Delphinidin, Ameliorates Psoriatic Features In Vitro and in an Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Disease in Mice.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2017 Jan 10;26(2):49-69. doi: 10.1089/ars.2016.6769. Epub 2016 Oct 4. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2017. PMID: 27393705 Free PMC article.
-
Central role of Yes-associated protein and WW-domain-containing transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif in pancreatic cancer development.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Apr 21;25(15):1797-1816. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i15.1797. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31057295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ERK inhibition sensitizes CZ415-induced anti-osteosarcoma activity in vitro and in vivo.Oncotarget. 2017 May 30;8(47):82027-82036. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18303. eCollection 2017 Oct 10. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29137241 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2011. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:212–36. - PubMed
-
- Shimobayashi M, Hall MN. Making new contacts: the mTOR network in metabolism and signalling crosstalk. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15:155–62. - PubMed
-
- Asano T, Yao Y, Shin S, McCubrey J, Abbruzzese JL, Reddy SA. Insulin receptor substrate is a mediator of phosphoinositide 3-kinase activation in quiescent pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2005;65:9164–8. - PubMed
-
- Eser S, Reiff N, Messer M, Seidler B, Gottschalk K, Dobler M, et al. Selective requirement of PI3K/PDK1 signaling for Kras oncogene-driven pancreatic cell plasticity and cancer. Cancer Cell. 2013;23:406–20. - PubMed
-
- Asano T, Yao Y, Zhu J, Li D, Abbruzzese JL, Reddy SA. The rapamycin analog CCI-779 is a potent inhibitor of pancreatic cancer cell proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;331:295–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

