Detection of pancreatic cancer biomarkers using mass spectrometry
- PMID: 25673969
- PMCID: PMC4285963
- DOI: 10.4137/CIN.S16341
Detection of pancreatic cancer biomarkers using mass spectrometry
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic cancer is the fourth leading cause of cancer-related deaths. Therefore, in order to improve survival rates, the development of biomarkers for early diagnosis is crucial. Recently, diabetes has been associated with an increased risk of pancreatic cancer. The aims of this study were to search for novel serum biomarkers that could be used for early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer and to identify whether diabetes was a risk factor for this disease.
Methods: Blood samples were collected from 25 patients with diabetes (control) and 93 patients with pancreatic cancer (including 53 patients with diabetes), and analyzed using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF/MS). We performed preprocessing, and various classification methods with imputation were used to replace the missing values. To validate the selection of biomarkers identified in pancreatic cancer patients, we measured biomarker intensity in pancreatic cancer patients with diabetes following surgical resection and compared our results with those from control (diabetes-only) patients.
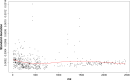
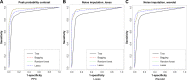
Results: By using various classification methods, we identified the commonly splitting protein peaks as m/z 1,465, 1,206, and 1,020. In the follow-up study, in which we assessed biomarkers in pancreatic cancer patients with diabetes after surgical resection, we found that the intensities of m/z at 1,465, 1,206, and 1,020 became comparable with those of diabetes-only patients.
Keywords: biomarker; classification; mass spectrometry; pancreatic cancer.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Pancreatic cancer biomarkers discovery by surface-enhanced laser desorption and ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2009;47(6):713-23. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2009.158. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2009. PMID: 19426140
-
Serum peptidome profiling revealed platelet factor 4 as a potential discriminating Peptide associated with pancreatic cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Jun 1;15(11):3812-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2701. Epub 2009 May 26. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19470732
-
Biomarkers screening between preoperative and postoperative patients in pancreatic cancer.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(7):4161-5. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.7.4161. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013. PMID: 23991970
-
Biomarker Characterization by MALDI-TOF/MS.Adv Clin Chem. 2015;69:209-54. doi: 10.1016/bs.acc.2015.01.001. Epub 2015 Feb 17. Adv Clin Chem. 2015. PMID: 25934363 Review.
-
Protein profiling for cancer biomarker discovery using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry and infrared imaging: a review.Anal Chim Acta. 2011 Mar 25;690(1):26-34. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2011.01.044. Epub 2011 Mar 2. Anal Chim Acta. 2011. PMID: 21414433 Review.
Cited by
-
Label-free differentiation of human pancreatic cancer, pancreatitis, and normal pancreatic tissue by molecular spectroscopy.J Biomed Opt. 2022 Jul 25;27(7):75001. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.27.7.075001. J Biomed Opt. 2022. PMID: 36399853 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-to-cell interaction analysis of prognostic ligand-receptor pairs in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021 Sep 4;28:101126. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.101126. eCollection 2021 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021. PMID: 34522794 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a MALDI MS-based platform for early detection of acute kidney injury.Proteomics Clin Appl. 2016 Jul;10(7):732-42. doi: 10.1002/prca.201500117. Epub 2016 May 17. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2016. PMID: 27119821 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Application of Proteomics in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Biomarker Investigations: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 14;23(4):2093. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042093. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SWATH-MS based proteomic profiling of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tumours reveals the interplay between the extracellular matrix and related intracellular pathways.PLoS One. 2020 Oct 13;15(10):e0240453. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240453. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33048956 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

