COPD: balancing oxidants and antioxidants
- PMID: 25673984
- PMCID: PMC4321570
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S42414
COPD: balancing oxidants and antioxidants
Abstract
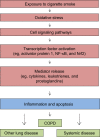
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is one of the most common chronic illnesses in the world. The disease encompasses emphysema, chronic bronchitis, and small airway obstruction and can be caused by environmental exposures, primarily cigarette smoking. Since only a small subset of smokers develop COPD, it is believed that host factors interact with the environment to increase the propensity to develop disease. The major pathogenic factors causing disease include infection and inflammation, protease and antiprotease imbalance, and oxidative stress overwhelming antioxidant defenses. In this review, we will discuss the major environmental and host sources for oxidative stress; discuss how oxidative stress regulates chronic bronchitis; review the latest information on genetic predisposition to COPD, specifically focusing on oxidant/antioxidant imbalance; and review future antioxidant therapeutic options for COPD. The complexity of COPD will necessitate a multi-target therapeutic approach. It is likely that antioxidant supplementation and dietary antioxidants will have a place in these future combination therapies.
Keywords: Chinese herbs; acupuncture; cigarette smoking; dietary antioxidants; gene regulation; mucins.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pulmonary and systemic oxidant/antioxidant imbalance in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2005;2(1):50-60. doi: 10.1513/pats.200411-056SF. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2005. PMID: 16113469 Review.
-
Oxidative stress and free radicals in COPD--implications and relevance for treatment.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2014 Oct 17;9:1207-24. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S51226. eCollection 2014. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2014. PMID: 25378921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidants and COPD.Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2005 Dec;4(6):627-41. doi: 10.2174/156801005774912815. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2005. PMID: 17305519 Review.
-
Oxidants/antioxidants and COPD.Chest. 2000 May;117(5 Suppl 1):303S-17S. doi: 10.1378/chest.117.5_suppl_1.303s-a. Chest. 2000. PMID: 10843965 Review.
-
Current perspectives of oxidative stress and its measurement in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.COPD. 2010 Aug;7(4):291-306. doi: 10.3109/15412555.2010.496818. COPD. 2010. PMID: 20673039 Review.
Cited by
-
A flavanone from Baccharis retusa (Asteraceae) prevents elastase-induced emphysema in mice by regulating NF-κB, oxidative stress and metalloproteinases.Respir Res. 2015 Jun 30;16(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12931-015-0233-3. Respir Res. 2015. PMID: 26122092 Free PMC article.
-
A Mitochondrial Perspective of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Pathogenesis.Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2016 Oct;79(4):207-213. doi: 10.4046/trd.2016.79.4.207. Epub 2016 Oct 5. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2016. PMID: 27790272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Machine-Learning Algorithm-Based Prediction of Diagnostic Gene Biomarkers Related to Immune Infiltration in Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 8;13:740513. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.740513. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35350787 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of Oxidative Stress in COPD.Curr Health Sci J. 2018 Jan-Mar;44(1):48-55. doi: 10.12865/CHSJ.44.01.08. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Curr Health Sci J. 2018. PMID: 30622755 Free PMC article.
-
l-Menthol alleviates cigarette smoke extract induced lung injury in rats by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation via nuclear factor kappa B, p38 MAPK and Nrf2 signalling pathways.RSC Adv. 2018 Mar 5;8(17):9353-9363. doi: 10.1039/c8ra00160j. eCollection 2018 Feb 28. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35541889 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hogg JC, Chu F, Utokaparch S, et al. The nature of small-airway obstruction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(26):2645–2653. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

