The impact of IGF-1R expression on the outcomes of patients with breast cancer: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 25674003
- PMCID: PMC4321663
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S74774
The impact of IGF-1R expression on the outcomes of patients with breast cancer: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: The value of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) for predicting survival of patients with breast cancer remains controversial. The purpose of this study was to perform a meta-analysis of the published data to attempt to clarify the impact of IGF-1R.
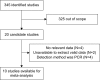
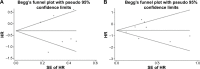
Methods: Studies published between January 1, 1990 and October 1, 2014 were identified using an electronic search to aggregate the available survival results. Studies were included if they reported detecting IGF-1R expression in the primary breast cancer and analyzed patient survival data according to IGF-1R status. The principal outcome measures were hazard ratios (HRs) for survival of IGF-1R-positive patients. Combined HRs and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were estimated using fixed- or random-effects models according to between-study heterogeneity.
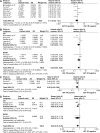
Results: Ten studies, involving 5,406 patients, satisfied our inclusion criteria. Data from five studies provided the impact of IGF-1R on overall survival (OS), three studies the impact on breast cancer-specific survival (BCSS), and seven studies the impact on disease-free survival (DFS). The results of meta-analysis showed that for DFS, membranous IGF-1R positivity was not a significant predictor. The combined HR for OS/BCSS was 0.63 (95% CI: 0.42-0.95, P=0.03), indicating that membranous IGF-1R positivity was a significant predictor of better survival. IGF-1R cytoplasmic positivity was significantly associated with longer DFS and OS/BCSS (combined HR: 0.56, 95% CI: 0.35-0.89, P=0.01; combined HR: 0.55, 95% CI: 0.35-0.85, P=0.008, respectively). The results of subgroup analysis suggested that membranous IGF-1R positivity in hormone-receptor-positive breast cancer was correlated with favorable DFS (combined HR: 0.61, 95% CI: 0.41-0.92, P=0.02) and OS/BCSS (combined HR: 0.73, 95% CI: 0.57-0.93, P=0.01). Membranous IGF-1R positivity in triple-negative breast cancer predicted worse DFS (combined HR: 1.86, 95% CI: 1.03-3.34, P=0.04). Membranous IGF-1R positivity in Her-2-positive or ER (estrogen receptor)-negative breast cancer was not found to be a significant prognostic indicator.
Conclusion: The results of this meta-analysis suggest that IGF-1R expression has different prognostic values for patients with breast cancers of different molecular subtypes. It was a favorable prognostic indicator in unselected breast cancers and hormone-receptor-positive cancers, but indicated poor survival in triple-negative breast cancers.
Keywords: IGF-1R; breast cancer; disease-free survival; hazard ratio; meta-analysis; overall survival; prognosis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Addition of zoledronic acid to neoadjuvant chemotherapy is not beneficial in patients with HER2-negative stage II/III breast cancer: 5-year survival analysis of the NEOZOTAC trial (BOOG 2010-01).Breast Cancer Res. 2019 Aug 28;21(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s13058-019-1180-6. Breast Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31455425 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of estrogen receptor-β expression on breast cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016 Feb;156(1):149-62. doi: 10.1007/s10549-016-3721-3. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016. PMID: 26902609
-
Prognostic value of IGF-1R in lung cancer: A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 May;98(19):e15467. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015467. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31083179 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor expression in breast cancer tissue and mammographic density.Mol Clin Oncol. 2015 May;3(3):572-580. doi: 10.3892/mco.2015.497. Epub 2015 Jan 27. Mol Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26137269 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of chemokine receptor CXCR4 on breast cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis.Cancer Epidemiol. 2013 Oct;37(5):725-31. doi: 10.1016/j.canep.2013.04.017. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Cancer Epidemiol. 2013. PMID: 23763828 Review.
Cited by
-
The Insulin-like Growth Factor Axis, Adipokines, Physical Activity, and Obesity in Relation to Breast Cancer Incidence and Recurrence.Cancer Clin Oncol. 2015;4(2):24-31. doi: 10.5539/cco.v4n2p24. Cancer Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26251693 Free PMC article.
-
Mammographic density and breast tissue expression of inflammatory markers, growth factors, and vimentin.BMC Cancer. 2018 Nov 29;18(1):1191. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-5088-9. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30497427 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between apolipoprotein E gene ε2/ε3/ε4 polymorphism and breast cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Mar 7;9:1241-9. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S94228. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27022282 Free PMC article.
-
The arginine methyltransferase PRMT1 regulates IGF-1 signaling in breast cancer.Oncogene. 2019 May;38(21):4015-4027. doi: 10.1038/s41388-019-0694-9. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Oncogene. 2019. PMID: 30692633 Free PMC article.
-
Activation Versus Inhibition of IGF1R: A Dual Role in Breast Tumorigenesis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 17;13:911079. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.911079. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35784559 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, et al. GLOBOCAN 2008 v20 Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No 10 (Internet) Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2010. [Accessed December 2, 2014]. Available from: http://globocan.iarc.fr.
-
- Kamangar F, Dores GM, Anderson WF. Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five continents: defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in different geographic regions of the world. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(14):2137–2150. - PubMed
-
- Singh P, Alex JM, Bast F. Insulin receptor (IR) and insulin-like growth factor receptor 1(IGF-1R) signaling systems: novel treatment strategies for cancer. Med Oncol. 2014;31(1):805. - PubMed
-
- Negi A, Ramarao P, Kumar R. Recent advancements in small molecule inhibitors of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) tyrosine kinase as anticancer agents. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2013;13(5):653–681. - PubMed
-
- Bonneterre J, Peyrat JP, Beuscart R, et al. Prognostic significance of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptors in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1990;50(21):6931–6935. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

