fNIRS-based brain-computer interfaces: a review
- PMID: 25674060
- PMCID: PMC4309034
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2015.00003
fNIRS-based brain-computer interfaces: a review
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum "fNIRS-based brain-computer interfaces: a review".Front Hum Neurosci. 2015 Mar 26;9:172. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2015.00172. eCollection 2015. Front Hum Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25859210 Free PMC article.
Abstract
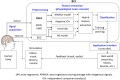
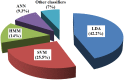
A brain-computer interface (BCI) is a communication system that allows the use of brain activity to control computers or other external devices. It can, by bypassing the peripheral nervous system, provide a means of communication for people suffering from severe motor disabilities or in a persistent vegetative state. In this paper, brain-signal generation tasks, noise removal methods, feature extraction/selection schemes, and classification techniques for fNIRS-based BCI are reviewed. The most common brain areas for fNIRS BCI are the primary motor cortex and the prefrontal cortex. In relation to the motor cortex, motor imagery tasks were preferred to motor execution tasks since possible proprioceptive feedback could be avoided. In relation to the prefrontal cortex, fNIRS showed a significant advantage due to no hair in detecting the cognitive tasks like mental arithmetic, music imagery, emotion induction, etc. In removing physiological noise in fNIRS data, band-pass filtering was mostly used. However, more advanced techniques like adaptive filtering, independent component analysis (ICA), multi optodes arrangement, etc. are being pursued to overcome the problem that a band-pass filter cannot be used when both brain and physiological signals occur within a close band. In extracting features related to the desired brain signal, the mean, variance, peak value, slope, skewness, and kurtosis of the noised-removed hemodynamic response were used. For classification, the linear discriminant analysis method provided simple but good performance among others: support vector machine (SVM), hidden Markov model (HMM), artificial neural network, etc. fNIRS will be more widely used to monitor the occurrence of neuro-plasticity after neuro-rehabilitation and neuro-stimulation. Technical breakthroughs in the future are expected via bundled-type probes, hybrid EEG-fNIRS BCI, and through the detection of initial dips.
Keywords: brain-computer interface; brain-machine interface; feature classification; feature extraction; functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS); physiological noise.
Figures


References
-
- Abibullaev B., An J., Moon J. I. (2011). Neural network classification of brain hemodynamic responses from four mental tasks. Int. J. Optomechatronics 5, 340–359 10.1080/15599612.2011.633209 - DOI
-
- Adhika D. R., Hazrati M. K., Hofmann U. G. (2012). An experimental setup for brain activity measurement based on near infrared spectroscopy. Biomed. Tech. 57, 609–612 10.1515/bmt-2012-4487 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

