Epithelioid angiosarcoma of the ilium: a case report
- PMID: 25674295
- PMCID: PMC4313960
Epithelioid angiosarcoma of the ilium: a case report
Abstract
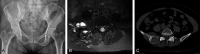
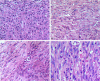
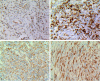
Bone epithelioid angiosarcoma (EA) is rare and characterized by large, mildly to moderately pleomorphic epithelioid cells, with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, vesicular nuclei, and prominent nucleoli. The tumors may arise in various locations in bone and the patients may present with unifocal or multifocal osseous disease. We present a unifocal lesion case of EA of the ilium in a 62-year-old woman. A needle biopsy of the ilium was performed and first diagnosed poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma based on CKpan and CK18 immunopositivity. The tumor was treated initially with curettage followed by chemotherapy. The final diagnosis on the surgical specimen was epithelioid angiosarcoma.
Keywords: Epithelioid angiosarcoma; bone.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epithelioid angiosarcoma at chest wall which needs to be carefully distinguished from malignant mesothelioma: report of a rare case.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Dec 1;7(12):9056-60. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25674287 Free PMC article.
-
Multicentric contiguous variant of epithelioid angiosarcoma of the bone. A rare variant showing angiotropic spread.Ann Diagn Pathol. 2005 Feb;9(1):33-7. doi: 10.1053/j.anndiagpath.2004.10.005. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2005. PMID: 15692948
-
Multicentric epithelioid angiosarcoma of the spine: a case report of a rare bone tumor.Spine J. 2007 Nov-Dec;7(6):716-9. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2006.08.013. Epub 2006 Dec 22. Spine J. 2007. PMID: 17998131
-
Primary Epithelioid Angiosarcoma of Bone with Robust Cell Cycle Progression and High Expression of SPARC: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2015 Spring;45(3):360-5. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2015. PMID: 26116605 Review.
-
Signet ring cell angiosarcoma: a hitherto unreported pitfall in the diagnosis of epithelioid cutaneous malignancies.Am J Dermatopathol. 2013 Aug;35(6):671-5. doi: 10.1097/DAD.0b013e3182892261. Am J Dermatopathol. 2013. PMID: 23538897 Review.
Cited by
-
Primary epithelioid angiosarcoma of right hip joint: A case report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Apr;97(15):e0307. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010307. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29642158 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Verbeke SL, Bertoni F, Bacchini P, Sciot R, Fletcher CD, Kroon HM, Hogendoorn PC, Bovee JV. Distinct histological features characterize primary angiosarcoma of bone. Histopathology. 2011;58:254–264. - PubMed
-
- Deshpande V, Rosenberg AE, O’Connell JX, Nielsen GP. Epithelioid angiosarcoma of the bone: a series of 10 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003;27:709–716. - PubMed
-
- Saglik Y, Yildiz Y, Atalar H, Basarir K. Primary angiosarcoma of the fibula: a case report. Acta Orthop Belg. 2007;73:799–803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
