Areca nut and its role in oral submucous fibrosis
- PMID: 25674328
- PMCID: PMC4312688
- DOI: 10.4317/jced.51318
Areca nut and its role in oral submucous fibrosis
Abstract
Areca nut, commonly called as betel nut or supari, is a fruit of areca catechu palm tree, which is native of South Asia and Pacific Islands. The seed or endosperm is consumed fresh, boiled or after sun drying or curing. Chewing areca nut is thought to have central nervous system stimulating effect and along with this it is known to have salivary stimulating and digestive properties. According to the traditional Ayurvedic medicine, chewing areca nut and betel leaf is a good remedy against halitosis. It is also used for its deworming property. Along with these beneficial effects of areca nut one of its most harmful effects on the human body in general and oral cavity in particular is the development of potentially malignant disorder called Oral Submucous Fibrosis. The present paper discusses in detail the effects of the components of areca nut on pathogenesis of Oral Submucous Fibrosis. Key words:Areca nut, oral submucous fibrosis, potentially malignant disorder, supari.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



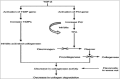
References
-
- Areca nut . Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia : 2012. [ cited 17 February 2012 ]. [Internet] Available from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Areca_nut .
-
- Angadi PV, Rao S. Areca nut in pathogenesis of oral submucous fibrosis: revisited. Oral MaxillofacSurg. 2011;15:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Betel chewing . Singapore : Singapore Infopedia ; 1999.
-
- Chandra GP, Ray CS. Epidemiology of betel quid usage. AnnAcad Med Singap. 2004;33:31–6. - PubMed
-
- Paan. Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia : 2008. [ cited 24 February 2012 ]. [Internet] Available from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paan .
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
