Treatment of chronic hepatitis C in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection
- PMID: 25674512
- PMCID: PMC4308522
- DOI: 10.5501/wjv.v4.i1.1
Treatment of chronic hepatitis C in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection
Abstract
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is one of the most frequent causes of comorbidity and mortality in the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) population, and liver-related mortality is now the second highest cause of death in HIV-positive patients, so HCV infection should be countered with adequate antiviral therapy. In 2011 began the era of directly acting antivirals (DAAs) and the HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitors telaprevir and boceprevir were approved to treat HCV-genotype-1 infection, each one in combination with pegylated interferon alfa (Peg-IFN) + ribavirin (RBV). The addition of the first generation DAAs, strongly improved the efficacy of antiviral therapy in patients with HCV-genotype 1, both for the HCV-monoinfected and HIV/HCV coinfected, and the poor response to Peg-IFN + RBV in HCV/HIV coinfection was enhanced. These treatments showed higher rates of sustained virological response than Peg-IFN + RBV but reduced tolerability and adherence due to the high pill burden and the several pharmacokinetic interactions between HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitors and antiretroviral drugs. Then in 2013 a new wave of DAAs arrived, characterized by high efficacy, good tolerability, a low pill burden and shortened treatment duration. The second and third generation DAAs also comprised IFN-free regimens, which in small recent trials on HIV-positive patients have shown comforting preliminary results in terms of efficacy, tolerability and adherence.
Keywords: Anti-hepatitis C virus treatment; Chronic hepatitis C; Directly acting antivirals; HIV/HCV coinfection; Hepatitis C virus infection; Human immunode-ficiency virus infection.
Figures
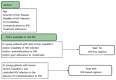

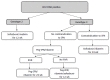
References
-
- Wandeler G, Gsponer T, Bregenzer A, Günthard HF, Clerc O, Calmy A, Stöckle M, Bernasconi E, Furrer H, Rauch A. Hepatitis C virus infections in the Swiss HIV Cohort Study: a rapidly evolving epidemic. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;55:1408–1416. - PubMed
-
- van der Helm JJ, Prins M, del Amo J, Bucher HC, Chêne G, Dorrucci M, Gill J, Hamouda O, Sannes M, Porter K, et al. The hepatitis C epidemic among HIV-positive MSM: incidence estimates from 1990 to 2007. AIDS. 2011;25:1083–1091. - PubMed
-
- Garten RJ, Lai S, Zhang J, Liu W, Chen J, Vlahov D, Yu XF. Rapid transmission of hepatitis C virus among young injecting heroin users in Southern China. Int J Epidemiol. 2004;33:182–188. - PubMed
-
- Puoti M, Manno D, Nasta P, Carosi G. The burden of HIV and hepatitis C virus coinfection. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2007;2:460–465. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

