A Prospective Screening of HLA-B*57.01 Allelic Variant for Preventing the Hypersensivity Reaction to Abacavir: Experience from the Laboratory of Molecular Biology of the Infectious Diseases Division at the University Hospital of Salerno
- PMID: 25674551
- PMCID: PMC4309657
A Prospective Screening of HLA-B*57.01 Allelic Variant for Preventing the Hypersensivity Reaction to Abacavir: Experience from the Laboratory of Molecular Biology of the Infectious Diseases Division at the University Hospital of Salerno
Abstract
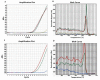
Abacavir is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor largely used as part of the antiretroviral therapy in Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)-infected patients. Some individuals (2-9%) who start an abacavir treatment show an immunologic reaction indicated as hypersensitivity reaction syndrome (HSR) that is often responsible for therapy discontinuation and could represent a life-threatening event. Some studies demonstrated a correlation between this adverse reaction and the class I of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) allele, HLA-B*57.01, in several populations, including Caucasians. Nowadays, International HIV treatment guidelines recommend the HLA-B*57.01 genotyping before abacavir administration to reduce the incidence of HSR. Both male and female HIV-infected patients were enrolled at the Infectious Diseases Division at the University Hospital of Salerno, and admitted to a prospective HLAB*57.01 screening. Genetic analysis was carried out through two sequential Real-Time PCR reactions in which Sybr-Green was used. Out of 248 patients, 215 were Italians from Southern Italy and 33 were coming from several non-EU members countries. All were genotyped: 6 Italians (2.8%) and 1 of the non-EU group (3%) were identified as HLAB*57.01 carriers. In this paper we present our experience in the field of abacavir pharmacogenetic and confirm the importance of Real Time PCR as a valid and cost-effective HLA-B*57.01 typing methodology.
Keywords: Abacavir; HIV; HLA-B*57.01; Real-Time PCR; hypersensitivity reaction.
Figures
References
-
- Guidelines for the Use of Antiretroviral Agents in HIV infection. [Internet]. Available from: http://aidsinfo.nih.gov/guidelines.
-
- Hetherington S, Hughes AR, Mosteller M, et al. Genetic variations in HLA-B region and hypersensitivity reactions to abacavir. Lancet. 2002;359(9312):1121–2. - PubMed
-
- Mallal S, Nolan D, Witt C, et al. Association between presence of HLA-B*5701, HLA-DR7, and HLA-DQ3 and hypersensitivity to HIV-1 reverse-transcriptase inhibitor abacavir. Lancet. 2002;359(9308):727–32. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials