Case series of lipid accumulation in the human corpus cavernosum
- PMID: 25674764
- PMCID: PMC4602761
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000550
Case series of lipid accumulation in the human corpus cavernosum
Abstract
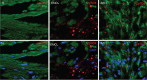
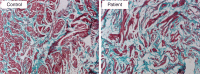
Erectile dysfunction is a prevalent problem affecting millions of men in the United States and around the world. There have been no reports of the presence of lipids within the human penile corporal bodies, whether in normal or diseased states. We present here a case series of 9 patients who underwent penile corporal tissue biopsy during penile prosthesis insertion with severe intracorporal fibrosis and difficulties during insertion.Oil Red O staining was done to identify lipids; LipidTOX and phalloidin double staining was used to identify lipid location within the corpora, and Masson's trichrome staining was done to assess fibrosis.We identified lipid accumulation in those 9 corporal tissue samples, and further analysis showed the distribution to be 10% intramyocellular lipids and 90% extramyocellular lipids. These 9 specimens contained increased amount of collagen when compared with controls. In addition, we analyzed corporal samples from 10 random erectile dysfunction patients presenting for penile prosthesis insertion and identified no lipid accumulation in those control patients.This is the first report of lipid accumulation in the human corpus cavernosum. Possible mechanisms of lipid accumulation include androgen deficiency and dedifferentiation of corpus smooth muscle cells into other phenotypes; however, the exact mechanism is unknown and further research is needed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparative study between corpus cavernosum-electromyography findings and electron microscopy of cavernosal muscle biopsies in erectile dysfunction patients.Int J Urol. 1998 May;5(3):252-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.1998.tb00599.x. Int J Urol. 1998. PMID: 9624557
-
Reduced corporal fibrosis to protect erectile function by inhibiting the Rho-kinase/LIM-kinase/cofilin pathway in the aged transgenic rat harboring human tissue kallikrein 1.Asian J Androl. 2017 Jan-Feb;19(1):67-72. doi: 10.4103/1008-682X.189209. Asian J Androl. 2017. PMID: 27678468 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced glycation end products in human penis: elevation in diabetic tissue, site of deposition, and possible effect through iNOS or eNOS.Urology. 1997 Dec;50(6):1016-26. doi: 10.1016/S0090-4295(97)00512-8. Urology. 1997. PMID: 9426743
-
Critical Appraisal and Review of Management Strategies for Severe Fibrosis During Penile Implant Surgery.J Sex Med. 2015 Nov;12 Suppl 7:439-47. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12985. J Sex Med. 2015. PMID: 26565574 Review.
-
Weapons of penile smooth muscle destruction: androgen deficiency promotes accumulation of adipocytes in the corpus cavernosum.Aging Male. 2005 Sep-Dec;8(3-4):141-6. doi: 10.1080/13685530500328183. Aging Male. 2005. PMID: 16390736 Review.
Cited by
-
Macrophage-Specific Toll Like Receptor 9 (TLR9) Causes Corpus Cavernosum Dysfunction in Mice Fed a High Fat Diet.J Sex Med. 2021 Apr;18(4):723-731. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2021.01.180. Epub 2021 Mar 16. J Sex Med. 2021. PMID: 33741290 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of low-intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy in an obesity-associated erectile dysfunction rat model.BJU Int. 2018 Jul;122(1):133-142. doi: 10.1111/bju.14202. Epub 2018 Apr 17. BJU Int. 2018. PMID: 29573106 Free PMC article.
-
Erectile Dysfunction: A Primer for in Office Management.Med Sci (Basel). 2019 Aug 29;7(9):90. doi: 10.3390/medsci7090090. Med Sci (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31470566 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ayta IA, McKinlay JB, Krane RJ. The likely worldwide increase in erectile dysfunction between 1995 and 2025 and some possible policy consequences. BJU Int 1999; 84:50–56. - PubMed
-
- NIH Consensus Conference. Impotence. NIH Consensus Development Panel on Impotence. JAMA 1993; 270:83–90. - PubMed
-
- Shamloul R, Ghanem H. Erectile dysfunction. Lancet 2013; 381:153–165. - PubMed
-
- Lewis RW, Fugl-Meyer KS, Corona G, et al. Original articles: definitions/epidemiology/risk factors for sexual dysfunction. J Sex Med 2010; 7:1598–1607. - PubMed
-
- Zimmet P, Alberti KGMM, Shaw J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature 2001; 414:872–877. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

