Herpes simplex virus suppresses necroptosis in human cells
- PMID: 25674983
- PMCID: PMC4382104
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.01.003
Herpes simplex virus suppresses necroptosis in human cells
Abstract
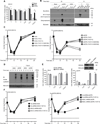
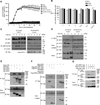
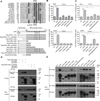
Herpes simplex virus (HSV)-1 and HSV-2 are significant human pathogens causing recurrent disease. During infection, HSV modulates cell death pathways using the large subunit (R1) of ribonucleotide reductase (RR) to suppress apoptosis by binding to and blocking caspase-8. Here, we demonstrate that HSV-1 and HSV-2 R1 proteins (ICP6 and ICP10, respectively) also prevent necroptosis in human cells by inhibiting the interaction between receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIP1) and RIP3, a key step in tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-induced necroptosis. We show that suppression of this cell death pathway requires an N-terminal RIP homotypic interaction motif (RHIM) within R1, acting in concert with the caspase-8-binding domain, which unleashes necroptosis independent of RHIM function. Thus, necroptosis is a human host defense pathway against two important viral pathogens that naturally subvert multiple death pathways via a single evolutionarily conserved gene product.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
HSV cheats the executioner.Cell Host Microbe. 2015 Feb 11;17(2):148-51. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.01.013. Cell Host Microbe. 2015. PMID: 25674981
References
-
- Bousfiha A, Picard C, Boisson-Dupuis S, Zhang SY, Bustamante J, Puel A, Jouanguy E, Ailal F, El-Baghdadi J, Abel L, et al. Primary immunodeficiencies of protective immunity to primary infections. Clin Immunol. 2010;135:204–209. - PubMed
-
- Brune W, Menard C, Heesemann J, Koszinowski UH. A ribonucleotide reductase homolog of cytomegalovirus and endothelial cell tropism. Science. 2001;291:303–305. - PubMed
-
- Chabaud S, Sasseville AM, Elahi SM, Caron A, Dufour F, Massie B, Langelier Y. The ribonucleotide reductase domain of the R1 subunit of herpes simplex virus type 2 ribonucleotide reductase is essential for R1 antiapoptotic function. J Gen Virol. 2007;88:384–394. - PubMed
-
- Chan FK, Shisler J, Bixby JG, Felices M, Zheng L, Appel M, Orenstein J, Moss B, Lenardo MJ. A role for tumor necrosis factor receptor-2 and receptor-interacting protein in programmed necrosis and antiviral responses. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:51613–51621. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

