Reflection impulsivity in binge drinking: behavioural and volumetric correlates
- PMID: 25678093
- PMCID: PMC4766871
- DOI: 10.1111/adb.12227
Reflection impulsivity in binge drinking: behavioural and volumetric correlates
Abstract
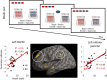
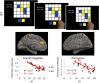
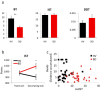
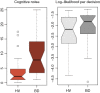
The degree to which an individual accumulates evidence prior to making a decision, also known as reflection impulsivity, can be affected in psychiatric disorders. Here, we study decisional impulsivity in binge drinkers, a group at elevated risk for developing alcohol use disorders, comparing two tasks assessing reflection impulsivity and a delay discounting task, hypothesizing impairments in both subtypes of impulsivity. We also assess volumetric correlates of reflection impulsivity focusing on regions previously implicated in functional magnetic resonance imaging studies. Sixty binge drinkers and healthy volunteers were tested using two different information-gathering paradigms: the beads task and the Information Sampling Task (IST). The beads task was analysed using a behavioural approach and a Bayesian model of decision making. Delay discounting was assessed using the Monetary Choice Questionnaire. Regression analyses of primary outcomes were conducted with voxel-based morphometry analyses. Binge drinkers sought less evidence prior to decision in the beads task compared with healthy volunteers in both the behavioural and computational modelling analysis. There were no group differences in the IST or delay discounting task. Greater impulsivity as indexed by lower evidence accumulation in the beads task was associated with smaller dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and inferior parietal volumes. In contrast, greater impulsivity as indexed by lower evidence accumulation in the IST was associated with greater dorsal cingulate and precuneus volumes. Binge drinking is characterized by impaired reflection impulsivity suggesting a deficit in deciding on the basis of future outcomes that are more difficult to represent. These findings emphasize the role of possible therapeutic interventions targeting decision-making deficits.
Keywords: Binge drinking; decision making; reflection impulsivity; voxel-based morphometry.
© 2015 The Authors. Addiction Biology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society for the Study of Addiction.
Figures
References
-
- Ashburner J (2007) A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. NeuroImage 38:95–113. - PubMed
-
- Beck A, Schlagenhauf F, Wustenberg T, Hein J, Kienast T, Kahnt T, Schmack K, Hagele C, Knutson B, Heinz A, Wrase J (2009) Ventral striatal activation during reward anticipation correlates with impulsivity in alcoholics. Biol Psychiatry 66:734–742. - PubMed
-
- Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelson M, Mock J, Erbaugh J (1961) An inventory for measuring depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 4:561–571. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

