A comparative examination of odontogenic gene expression in both toothed and toothless amniotes
- PMID: 25678399
- PMCID: PMC4401653
- DOI: 10.1002/jez.b.22594
A comparative examination of odontogenic gene expression in both toothed and toothless amniotes
Abstract
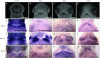
A well-known tenet of murine tooth development is that BMP4 and FGF8 antagonistically initiate odontogenesis, but whether this tenet is conserved across amniotes is largely unexplored. Moreover, changes in BMP4-signaling have previously been implicated in evolutionary tooth loss in Aves. Here we demonstrate that Bmp4, Msx1, and Msx2 expression is limited proximally in the red-eared slider turtle (Trachemys scripta) mandible at stages equivalent to those at which odontogenesis is initiated in mice, a similar finding to previously reported results in chicks. To address whether the limited domains in the turtle and the chicken indicate an evolutionary molecular parallelism, or whether the domains simply constitute an ancestral phenotype, we assessed gene expression in a toothed reptile (the American alligator, Alligator mississippiensis) and a toothed non-placental mammal (the gray short-tailed opossum, Monodelphis domestica). We demonstrate that the Bmp4 domain is limited proximally in M. domestica and that the Fgf8 domain is limited distally in A. mississippiensis just preceding odontogenesis. Additionally, we show that Msx1 and Msx2 expression patterns in these species differ from those found in mice. Our data suggest that a limited Bmp4 domain does not necessarily correlate with edentulism, and reveal that the initiation of odontogenesis in non-murine amniotes is more complex than previously imagined. Our data also suggest a partially conserved odontogenic program in T. scripta, as indicated by conserved Pitx2, Pax9, and Barx1 expression patterns and by the presence of a Shh-expressing palatal epithelium, which we hypothesize may represent potential dental rudiments based on the Testudinata fossil record.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures




References
-
- Åberg T, Wozney J, Thesleff I. Expression patterns of bone morphogenetic proteins (Bmps) in the developing mouse tooth suggest roles in morphogenesis and cell differentiation. Dev Dyn. 1997;210:383–396. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht UEG, Helms JA, Lin H. Visualization of gene expression patterns by in situ hybridization. In: Daston GP, editor. Molecular and Cellular Methods in Developmental Toxicology. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL: 1997. pp. 23–48.
-
- Bitgood MJ, McMahon AJ. Hedgehog and Bmp genes are coexpressed at many diverse sites of cell–cell interaction in the mouse embryo. Dev Biol. 1995;172:126–138. - PubMed
-
- Bei M, Kratochwil K, Maas RL. BMP4 rescues a non-cell-autonomous function of Msx1 in tooth development. Development. 2000;127:4711–4718. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

