Immobilizing osteogenic growth peptide with and without fibronectin on a titanium surface: effects of loading methods on mesenchymal stem cell differentiation
- PMID: 25678785
- PMCID: PMC4317146
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S74746
Immobilizing osteogenic growth peptide with and without fibronectin on a titanium surface: effects of loading methods on mesenchymal stem cell differentiation
Abstract
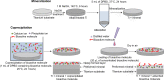
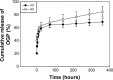
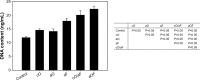
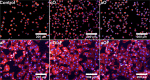
In this study, to improve the osseointegration of implants, osteogenic growth peptide (OGP) and fibronectin (FN) were loaded within mineral, which was formed on titanium, through adsorption and coprecipitation methods. The release profiles of OGP loaded by either adsorption or coprecipitation and the effects of the loading methods to immobilize OGP with and without FN on rat mesenchymal stem cell (rMSC) osteogenic differentiation were studied. The coprecipitation approach slightly reduced the initial burst release, while the adsorption approach provided a more sustained release. Dual loading of OGP and FN further improved cell attachments compared with either OGP or FN alone. Dually loaded OGP and FN also had a positive impact on rMSC proliferation and osteogenic differentiation. The difference in methods of loading OGP with and without FN also had some effects on osteogenic differentiation. Compared with coprecipitated OGP alone, adsorbed OGP enhanced later differentiation, such as osteocalcin secretion and matrix mineralization. Simultaneously adsorbed OGP and FN led to higher proliferation and higher osteogenic differentiation in both early and late stages compared with sequentially loaded OGP and FN. rMSC culture clearly indicated that simultaneously adsorbed OGP and FN could improve osseointegration, and this treatment represents a potential method for effective surface modification of dental and orthopedic implants.
Keywords: adsorption; coprecipitation; osseointegration.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Surface modification of TiO2 nanotubes with osteogenic growth peptide to enhance osteoblast differentiation.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017 Apr 1;73:490-497. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2016.12.083. Epub 2016 Dec 22. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017. PMID: 28183637
-
Multilayered pore-closed PLGA microsphere delivering OGP and BMP-2 in sequential release patterns for the facilitation of BMSCs osteogenic differentiation.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018 Jan;106(1):95-105. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.36210. Epub 2017 Sep 26. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018. PMID: 28884494
-
Role of Osteogenic Growth Peptide (OGP) and OGP(10-14) in Bone Regeneration: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Nov 22;17(11):1885. doi: 10.3390/ijms17111885. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27879684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Effects of osteogenic growth peptide to the proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2008 Nov;21(11):843-5. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2008. PMID: 19143249 Chinese.
-
Growth factor-functionalized titanium implants for enhanced bone regeneration: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Aug;274(Pt 2):133153. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.133153. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38897500 Review.
Cited by
-
Laminin functionalized biomimetic apatite to regulate the adhesion and proliferation behaviors of neural stem cells.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Oct 9;13:6223-6233. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S176596. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30349246 Free PMC article.
-
Nanolayer formation on titanium by phosphonated gelatin for cell adhesion and growth enhancement.Int J Nanomedicine. 2015 Sep 2;10:5597-607. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S82166. eCollection 2015. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015. PMID: 26366080 Free PMC article.
-
Covalently functionalized poly(etheretherketone) implants with osteogenic growth peptide (OGP) to improve osteogenesis activity.RSC Adv. 2020 Mar 6;10(17):9777-9785. doi: 10.1039/d0ra00103a. eCollection 2020 Mar 6. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35498607 Free PMC article.
-
Functional engineering strategies of 3D printed implants for hard tissue replacement.Regen Biomater. 2022 Nov 24;10:rbac094. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbac094. eCollection 2023. Regen Biomater. 2022. PMID: 36683758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kaempferol-immobilized titanium dioxide promotes formation of new bone: effects of loading methods on bone marrow stromal cell differentiation in vivo and in vitro.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Mar 19;13:1665-1676. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S150786. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29593412 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim H, Choi SH, Chung SM, Li LH, Lee IS. Enhanced bone forming ability of SLA-treated Ti coated with a calcium phosphate thin film formed by e-beam evaporation. Biomed Mater. 2010;5(4):044106. - PubMed
-
- Vandamme K, Holy X, Bensidhoum M, et al. In vivo molecular evidence of delayed titanium implant osseointegration in compromised bone. Biomaterials. 2011;32(14):3547–3554. - PubMed
-
- Tsukimura N, Yamada M, Iwasa F, et al. Synergistic effects of UV photofunctionalization and micro-nano hybrid topography on the biological properties of titanium. Biomaterials. 2011;32(19):4358–4368. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Lee IS, Cui FZ, Choi SH. The biocompatibility of nanostructured calcium phosphate coated on micro-arc oxidized titanium. Biomaterials. 2008;29(13):2025–2032. - PubMed
-
- Chen C, Qiu ZY, Zhang SM, Lee IS. Biomimetic fibronectin/mineral and osteogenic growth peptide/mineral composites synthesized on calcium phosphate thin films. Chem Commun (Camb) 2011;47(39):11056–11058. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

