Genetic interaction analysis of TCF7L2 for biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy in localized prostate cancer
- PMID: 25678841
- PMCID: PMC4323362
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.10953
Genetic interaction analysis of TCF7L2 for biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy in localized prostate cancer
Abstract
Backgroud: Accumulated evidence has demonstrated a significant role of the Wnt pathway in human prostate cancer. We hypothesize that genetic variants in the Wnt pathway effector, Transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2), may influence clinical outcomes in prostate cancer.
Methods: We comprehensively selected 12 tagged single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) to capture majority of common variants across TCF7L2, and genotyped in 458 localized prostate cancer patients treated with radical prostatectomy (RP). Kaplan-Meier analysis, Cox proportional hazard model, and survival tree analyses were performed to identify significant SNPs that correlated with biochemical recurrence (BCR) after surgery.
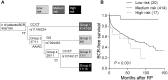
Results: A higher-order SNP-SNP interaction profile consisting of TCF7L2 rs7094463, rs10749127, and rs11196224 was significantly associated with BCR (P trend = 0.001). After adjusting for possible confounders, the genetic profile remained significant (P trend = 0.007). None of the studied SNPs were individually associated with BCR.
Conclusions: Our results support a genetic interaction in the TCF7L2 SNPs as a predictor of disease recurrence after curative RP in localized prostate cancer patients.
Keywords: TCF7L2; Wnt pathway; biochemical recurrence; prostate cancer; radical prostatectomy; single-nucleotide polymorphism.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Reya T, Clevers H. Wnt signalling in stem cells and cancer. Nature. 2005;434:843–50. - PubMed
-
- Iozzo RV, Eichstetter I, Danielson KG. Aberrant expression of the growth factor Wnt-5A in human malignancy. Cancer Res. 1995;55:3495–9. - PubMed
-
- Bao BY, Pao JB, Lin VC. et al. Individual and cumulative association of prostate cancer susceptibility variants with clinicopathologic characteristics of the disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2010;411:1232–7. - PubMed
-
- Huang SP, Huang LC, Ting WC. et al. Prognostic significance of prostate cancer susceptibility variants on prostate-specific antigen recurrence after radical prostatectomy. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2009;18:3068–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

