Role of TERRA in the regulation of telomere length
- PMID: 25678850
- PMCID: PMC4323371
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.10528
Role of TERRA in the regulation of telomere length
Abstract
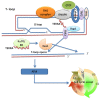
Telomere dysfunction is closely associated with human diseases such as cancer and ageing. Inappropriate changes in telomere length and/or structure result in telomere dysfunction. Telomeres have been considered to be transcriptionally silent, but it was recently demonstrated that mammalian telomeres are transcribed into telomeric repeat-containing RNA (TERRA). TERRA, a long non-coding RNA, participates in the regulation of telomere length, telomerase activity and heterochromatinization. The correct regulation of telomere length may be crucial to telomeric homeostasis and functions. Here, we summarize recent advances in our understanding of the crucial role of TERRA in the maintenance of telomere length, with focus on the variety of mechanisms by which TERRA is involved in the regulation of telomere length. This review aims to enable further understanding of how TERRA-targeted drugs can target telomere-related diseases.
Keywords: ALT; HDR; TERRA; protection of chromosome end; telomerase; telomere length.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Telomere functions grounding on TERRA firma.Trends Cell Biol. 2015 Jan;25(1):29-36. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2014.08.007. Epub 2014 Sep 23. Trends Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25257515 Review.
-
Telomeric noncoding RNA: telomeric repeat-containing RNA in telomere biology.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2014 May-Jun;5(3):407-19. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1220. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2014. PMID: 24523222 Review.
-
TERRA and Telomere Maintenance in the Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genes (Basel). 2023 Feb 28;14(3):618. doi: 10.3390/genes14030618. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36980890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased TERRA levels and RNase H sensitivity are conserved hallmarks of post-senescent survivors in budding yeast.Differentiation. 2018 Mar-Apr;100:37-45. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2018.02.002. Epub 2018 Feb 16. Differentiation. 2018. PMID: 29494831
-
DNA methylation mediated up-regulation of TERRA non-coding RNA is coincident with elongated telomeres in the human placenta.Mol Hum Reprod. 2016 Nov;22(11):791-799. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gaw053. Epub 2016 Sep 7. Mol Hum Reprod. 2016. PMID: 27604461
Cited by
-
LncRNAs-associated to genomic instability: A barrier to cancer therapy effectiveness.Front Genet. 2022 Nov 21;13:984329. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.984329. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36479250 Free PMC article.
-
Histone Modifications and the Maintenance of Telomere Integrity.Cells. 2019 Feb 25;8(2):199. doi: 10.3390/cells8020199. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30823596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Telomere biology: Rationale for diagnostics and therapeutics in cancer.RNA Biol. 2015;12(10):1078-82. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1081329. Epub 2015 Aug 20. RNA Biol. 2015. PMID: 26291128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory cytokine IL6 cooperates with CUDR to aggravate hepatocyte-like stem cells malignant transformation through NF-κB signaling.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 11;6:36843. doi: 10.1038/srep36843. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27833137 Free PMC article.
-
Telomeres and telomerase as therapeutic targets to prevent and treat age-related diseases.F1000Res. 2016 Jan 20;5:F1000 Faculty Rev-89. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.7020.1. eCollection 2016. F1000Res. 2016. PMID: 27081482 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- de Lange T. Shelterin: the protein complex that shapes and safeguards human telomeres. Genes Dev. 2005;19:2100–2110. - PubMed
-
- Palm W, de Lange T. How shelterin protects Mammalian telomeres. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2008;42:301–334. - PubMed
-
- Walker JR, Zhu XD. Post-translational modifications of TRF1 and TRF2 and their roles in telomere maintenance. Mech Ageing Dev. 2012;133:421–434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

