Proteomic signatures of serum albumin-bound proteins from stroke patients with and without endovascular closure of PFO are significantly different and suggest a novel mechanism for cholesterol efflux
- PMID: 25678897
- PMCID: PMC4305391
- DOI: 10.1186/1559-0275-12-2
Proteomic signatures of serum albumin-bound proteins from stroke patients with and without endovascular closure of PFO are significantly different and suggest a novel mechanism for cholesterol efflux
Abstract
Background: The anatomy of PFO suggests that it can allow thrombi and potentially harmful circulatory factors to travel directly from the venous to the arterial circulation - altering circulatory phenotype. Our previous publication using high-resolution LC-MS/MS to profile protein and peptide expression patterns in plasma showed that albumin was relatively increased in donor samples from PFO-related than other types of ischemic strokes. Since albumin binds a host of molecules and acts as a carrier for lipoproteins, small molecules and drugs, we decided to investigate the albumin-bound proteins (in a similar sample cohort) in an effort to unravel biological changes and potentially discover biomarkers related to PFO-related stroke and PFO endovascular closure.
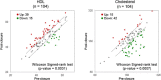
Methods: The method used in this study combined albumin immuno-enrichment with high resolution LC-MS in order to specifically capture and quantify the albumin-bound proteins. Subsequently, we measured cholesterol and HDL in a larger, separate cohort of PFO stroke patients, pre and post closure.
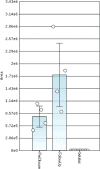
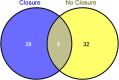
Results: The results demonstrated that a number of proteins were specifically associated with albumin in samples with and without endovascular closure of the PFO, and that the protein profiles were very different. Eight proteins, typically associated with HDL were common to both sample sets and quantitatively differently abundant. Pathway analysis of the MS results suggested that enhanced cholesterol efflux and reduced lipid oxidation were associated with PFO closure. Measurement of total cholesterol and HDL in a larger cohort of PFO closure samples using a colorimetric assay was consistent with the proteomic predictions.
Conclusions: The collective data presented in this study demonstrate that analysis of albumin-bound proteins could provide a valuable tool for biomarker discovery on the effects of PFO endovascular closure. In addition, the results suggest that PFO endovascular closure can potentially have effects on HDL, cholesterol and albumin-bound ApoA-I abundance, therefore possibly providing benefits in cardioprotective functions.
Keywords: Albumin; Biomarker; Cerebrovascular disease; Discovery; Ischemic stroke; Mass spectrometry; PFO; Patent foramen ovale; Proteomics; Stroke.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Heart-brain signaling in patent foramen ovale-related stroke: differential plasma proteomic expression patterns revealed with a 2-pass liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry discovery workflow.J Investig Med. 2012 Dec;60(8):1122-30. doi: 10.2310/JIM.0b013e318276de0e. J Investig Med. 2012. PMID: 23147404 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Risk of recurrent cerebrovascular events in patients with cryptogenic stroke or transient ischemic attack and patent foramen ovale: the FORI (Foramen Ovale Registro Italiano) study.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2011;31(2):109-16. doi: 10.1159/000321334. Epub 2010 Nov 17. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2011. PMID: 21088390
-
Long-Term Outcomes of Patent Foramen Ovale Closure or Medical Therapy after Stroke.N Engl J Med. 2017 Sep 14;377(11):1022-1032. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1610057. N Engl J Med. 2017. PMID: 28902590 Clinical Trial.
-
Patent foramen ovale: anatomy, outcomes, and closure.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2011 Mar;8(3):148-60. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2010.224. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21283148 Review.
-
Patent foramen ovale closure in the management of cryptogenic stroke: a review of current literature and guideline statements.Curr Med Res Opin. 2021 Mar;37(3):377-384. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2021.1876648. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Curr Med Res Opin. 2021. PMID: 33460329 Review.
Cited by
-
Macrophage infiltration promotes invasiveness of breast cancer cells via activating long non-coding RNA UCA1.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Aug 1;8(8):9052-61. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26464647 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing activities of oncogenic MIR17HG and tumor suppressive MIR100HG clusters and their gene targets regulate replicative senescence in human adult stem cells.NPJ Aging Mech Dis. 2017 Apr 20;3:7. doi: 10.1038/s41514-017-0006-y. eCollection 2017. NPJ Aging Mech Dis. 2017. PMID: 28649425 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and infarction patterns of PFO-related cryptogenic strokes and a prediction model.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2018 Sep 24;5(11):1323-1337. doi: 10.1002/acn3.647. eCollection 2018 Nov. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30480027 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of patent Foramen Ovale Closure for Refractory Epilepsy (PFOC-RE): a prospectively randomized control trial of an innovative surgical therapy for refractory epilepsy patients with PFO of high-grade right-to-left shunt.BMC Neurol. 2023 Jul 27;23(1):282. doi: 10.1186/s12883-023-03317-0. BMC Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37501155 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dysfunctional High-Density Lipoprotein: An Innovative Target for Proteomics and Lipidomics.Cholesterol. 2015;2015:296417. doi: 10.1155/2015/296417. Epub 2015 Nov 8. Cholesterol. 2015. PMID: 26634153 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Inglessis I, Elmariah S, Rengifo-Moreno PA, Margey R, O'Callaghan C, Cruz-Gonzalez I, Baron S, Mehrotra P, Tan TC, Hung J, Demirjian ZN, Buonanno FS, Ning M, Silverman SB, Cubeddu RJ, Pomerantsev E, Schainfeld RM, Dec GW, Jr, Palacios IF. Long-term experience and outcomes with transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2013;6:1176–83. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2013.06.013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lopez MF, Sarracino DA, Vogelsang M, Sutton JN, Athanas M, Krastins B, Garces A, Prakash A, Peterman S, Demirjian Z, Inglessis-Azuaje I, Feeney K, Elia M, McMullin D, Dec GW, Palacios I, Lo EH, Buonanno F, Ning M. Heart-brain signaling in patent foramen ovale-related stroke: differential plasma proteomic expression patterns revealed with a 2-pass liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry discovery workflow. J Investig Med. 2012;60:1122–30. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
