The effect of inversion times on the minimum signal intensity of the contrast agent concentration using inversion recovery t1-weighted fast imaging sequence
- PMID: 25679007
- PMCID: PMC4313446
The effect of inversion times on the minimum signal intensity of the contrast agent concentration using inversion recovery t1-weighted fast imaging sequence
Abstract
Background: Inversion recovery (IR) pulse sequences can generate T1-weighted images with a different range of inversion time (TI) to suppress or null the signal intensity (SI) for a specified tissue. In this study, we aimed to investigate the effect of TI values on the concentration of the contrast agent, which leads to a minimum signal intensity, using an inversion recovery T1-weighted 3-dimensional fast-gradient echo imaging sequence.
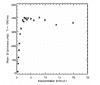
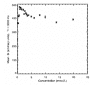
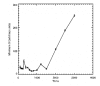
Methods: A phantom was designed to hold 25 vials which contained different (between 0 and 19.77mmol/L of (Gd-DTPA)) concentrations of the contrast agent. We used the vials of different concentrations to measure SI using IR sequences with different inversion times (TI, 100-3000ms).
Results: The results of this study revealed that the T1 recovery curve did not cross the x- axis for the lower TI. Therefore, a minimum SI can be observed from the concentration of the contrast agent versus SI curves. The findings of this study also revealed that the concentration of the contrast agent, which leads to a minimum SI, is dependent on the TI and the minimum SI will be increased at higher TI concentrations.
Conclusion: In conclusion, when the TI parameter is used to suppress the SI of the specified tissues in clinical studies (e.g., fat suppression or blood suppression in perfusion measurements), it should be chosen with great caution.
Keywords: Concentration of Contrast Agent; Inversion Time; Null Point; Signal Intensity; T1-Weighted.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Maximum and Minimum Signal Intensity and the Linear Relationship between Concentration and Signal Intensity in Saturation Recovery T1-weighted Images by use of a Turbo Fast Low-Angle Shot Sequence.J Biomed Phys Eng. 2020 Aug 1;10(4):449-458. doi: 10.31661/jbpe.v0i0.823. eCollection 2020 Aug. J Biomed Phys Eng. 2020. PMID: 32802793 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of iron oxide nanoparticles coating type on the relationship between nanoparticles concentration and signal intensity in inversion recovery T1-weighted MRI.Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2015 May 6;29:211. eCollection 2015. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2015. PMID: 26478869 Free PMC article.
-
Equilibrium signal intensity mapping, an MRI method for fast mapping of longitudinal relaxation rates and for image enhancement.Magn Reson Imaging. 2007 Jun;25(5):641-51. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2006.10.008. Epub 2006 Nov 21. Magn Reson Imaging. 2007. PMID: 17540275
-
Comparison of maximum signal intensity of contrast agent on t1-weighted images using spin echo, fast spin echo and inversion recovery sequences.Iran J Radiol. 2012 Dec;10(1):27-32. doi: 10.5812/iranjradiol.5452. Epub 2012 Dec 27. Iran J Radiol. 2012. PMID: 23599710 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Multiplied, Added, Subtracted and/or FiTted Inversion Recovery (MASTIR) pulse sequences.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2020 Jun;10(6):1334-1369. doi: 10.21037/qims-20-568. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2020. PMID: 32550142 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Maximum and Minimum Signal Intensity and the Linear Relationship between Concentration and Signal Intensity in Saturation Recovery T1-weighted Images by use of a Turbo Fast Low-Angle Shot Sequence.J Biomed Phys Eng. 2020 Aug 1;10(4):449-458. doi: 10.31661/jbpe.v0i0.823. eCollection 2020 Aug. J Biomed Phys Eng. 2020. PMID: 32802793 Free PMC article.
-
The Direction of Flow and Phase-encoding Schemes Effects on Signal Intensity in T1-weighted Inversion Recovery TurboFLASH Images.J Biomed Phys Eng. 2023 Feb 1;13(1):45-54. doi: 10.31661/jbpe.v0i0.2203-1468. eCollection 2023 Feb. J Biomed Phys Eng. 2023. PMID: 36818011 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning for the harmonization of structural MRI scans: a survey.Biomed Eng Online. 2024 Aug 31;23(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s12938-024-01280-6. Biomed Eng Online. 2024. PMID: 39217355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of iron oxide nanoparticles coating type on the relationship between nanoparticles concentration and signal intensity in inversion recovery T1-weighted MRI.Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2015 May 6;29:211. eCollection 2015. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2015. PMID: 26478869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Unger EC, Ugurbil K, Latchaw RE. Contrast agent for cerebral perfusion MR imaging. JMRI. 1994 May/June;4:235–42. - PubMed
-
- Nazarpoor M. The effect of repetition time on the maximum linear relationship between contrast agent concentration and signal intensity on T1 weighted image using inversion recovery (IR) sequence. Iran J Radiol. 2009 July;6(4):247–52.
-
- Martel A, Moody A, Allder S, Delay G, Morgan P. Extracting parametric images from dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI studies of the brain using factor analysis. Med Image Anal. 2001 Mar;5:29–39. - PubMed
-
- Nazarpoor M. Effects of inversion and saturation times on relationships between contrast agent concentrations and signal intensities of T1-weighted magnetic resonance images. Radiol Phys Technol. 2010 Feb;3:120–6. - PubMed
-
- Nazarpoor M, Mayabi Z, Shfaie A, Pesianian E, Aghaverdizadeh D. Maximum relationship between signal intensity and concentration of contrast agent in 03 T and 15 T using T1-weighted spin echo sequence Medical Journal of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences & Health services. 2011 Feb. /Mar;32(6):72–6. (Persian).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources