The transcription factor NFAT promotes exhaustion of activated CD8⁺ T cells
- PMID: 25680272
- PMCID: PMC4346317
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.01.006
The transcription factor NFAT promotes exhaustion of activated CD8⁺ T cells
Abstract
During persistent antigen stimulation, CD8(+) T cells show a gradual decrease in effector function, referred to as exhaustion, which impairs responses in the setting of tumors and infections. Here we demonstrate that the transcription factor NFAT controls the program of T cell exhaustion. When expressed in cells, an engineered form of NFAT1 unable to interact with AP-1 transcription factors diminished T cell receptor (TCR) signaling, increased the expression of inhibitory cell surface receptors, and interfered with the ability of CD8(+) T cells to protect against Listeria infection and attenuate tumor growth in vivo. We defined the genomic regions occupied by endogenous and engineered NFAT1 in primary CD8(+) T cells and showed that genes directly induced by the engineered NFAT1 overlapped with genes expressed in exhausted CD8(+) T cells in vivo. Our data show that NFAT promotes T cell anergy and exhaustion by binding at sites that do not require cooperation with AP-1.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
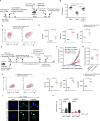

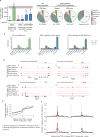

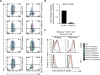
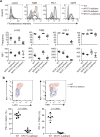
Comment in
-
The importance of cooperation: partnerless NFAT induces T cell exhaustion.Immunity. 2015 Feb 17;42(2):203-205. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.01.023. Immunity. 2015. PMID: 25692694
References
-
- Barber DL, Wherry EJ, Masopust D, Zhu B, Allison JP, Sharpe AH, Freeman GJ, Ahmed R. Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Nature. 2006;439:682–687. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- U19 AI109976/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA150975/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI109842/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA179563/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI072543/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA42471/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI040127/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR027366/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK043351/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI84167/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA042471/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA150975/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI084167/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI095634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI40127/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

