Subcellular localization and Ser-137 phosphorylation regulate tumor-suppressive activity of profilin-1
- PMID: 25681442
- PMCID: PMC4423694
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.619874
Subcellular localization and Ser-137 phosphorylation regulate tumor-suppressive activity of profilin-1
Abstract
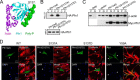
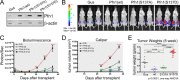
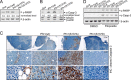
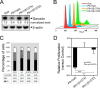
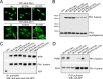
The actin-binding protein profilin-1 (Pfn1) inhibits tumor growth and yet is also required for cell proliferation and survival, an apparent paradox. We previously identified Ser-137 of Pfn1 as a phosphorylation site within the poly-l-proline (PLP) binding pocket. Here we confirm that Ser-137 phosphorylation disrupts Pfn1 binding to its PLP-containing ligands with little effect on actin binding. We find in mouse xenografts of breast cancer cells that mimicking Ser-137 phosphorylation abolishes cell cycle arrest and apoptotic sensitization by Pfn1 and confers a growth advantage to tumors. This indicates a previously unrecognized role of PLP binding in Pfn1 antitumor effects. Spatial restriction of Pfn1 to the nucleus or cytoplasm indicates that inhibition of tumor cell growth by Pfn1 requires its nuclear localization, and this activity is abolished by a phosphomimetic mutation on Ser-137. In contrast, cytoplasmic Pfn1 lacks inhibitory effects on tumor cell growth but rescues morphological and proliferative defects of PFN1 null mouse chondrocytes. These results help reconcile seemingly opposed cellular effects of Pfn1, provide new insights into the antitumor mechanism of Pfn1, and implicate Ser-137 phosphorylation as a potential therapeutic target for breast cancer.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cancer; Cell Compartmentalization; Nucleus; Phosphorylation; Profilin; Proliferation.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Birbach A. (2008) Profilin, a multi-modal regulator of neuronal plasticity. Bioessays 30, 994–1002 - PubMed
-
- Jockusch B. M., Murk K., Rothkegel M. (2007) The profile of profilins. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 159, 131–149 - PubMed
-
- Schlüter K., Jockusch B. M., Rothkegel M. (1997) Profilins as regulators of actin dynamics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1359, 97–109 - PubMed
-
- Witke W. (2004) The role of profilin complexes in cell motility and other cellular processes. Trends Cell Biol. 14, 461–469 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50 CA094056/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS056114/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS057105/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA064786/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA131226/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54CA112970/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA143836/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54CA143836/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA140663/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA91842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA131226/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37CA064786/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS50284/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA112970/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA091842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS050284/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA143233/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA94056/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA057621/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA140663/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA057621/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA143233/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

