Antiproliferative activity of long chain acylated esters of quercetin-3-O-glucoside in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells
- PMID: 25681471
- PMCID: PMC4935297
- DOI: 10.1177/1535370215570828
Antiproliferative activity of long chain acylated esters of quercetin-3-O-glucoside in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells
Abstract
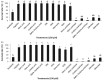
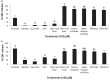
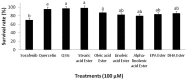
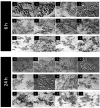
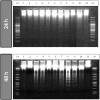
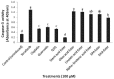
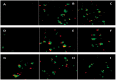
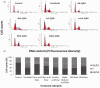
Despite their strong role in human health, poor bioavailability of flavonoids limits their biological effects in vivo. Enzymatically catalyzed acylation of fatty acids to flavonoids is one of the approaches of increasing cellular permeability and hence, biological activities. In this study, six long chain fatty acid esters of quercetin-3-O-glucoside (Q3G) acylated enzymatically and were used for determining their antiproliferative action in hepatocellular carcinoma cells (HepG2) in comparison to precursor compounds and two chemotherapy drugs (Sorafenib and Cisplatin). Fatty acid esters of Q3G showed significant inhibition of HepG2 cell proliferation by 85 to 90% after 6 h and 24 h of treatment, respectively. The cell death due to these novel compounds was associated with cell-cycle arrest in S-phase and apoptosis observed by DNA fragmentation, fluorescent microscopy and elevated caspase-3 activity and strong DNA topoisomerase II inhibition. Interestingly, Q3G esters showed significantly low toxicity to normal liver cells than Sorafenib (P < 0.05), a chemotherapy drug for hepatocellular carcinoma. Among all, oleic acid ester of Q3G displayed the greatest antiproliferation action and a high potential as an anti-cancer therapeutic. Overall, the results of the study suggest strong antiproliferative action of these novel food-derived compounds in treatment of cancer.
Keywords: HepG2 cells; Quercetin-3-O-glucoside; acylation; apoptosis; cancer; caspase-3; cell cycle; chemotherapy; hepatocellular carcinoma; topoisomerase II.
© 2015 by the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine.
Figures
References
-
- Rupasinghe HPV, Nair S, Robinson R. Chemopreventive properties of fruit phenolics and their possible mode of actions. In: Atta-Ur-Rahman (ed.). Studies in natural products chemistry 2014; Vol 42Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers, pp. 229–66.
-
- Arts IC, Hollman PC, De Mesquita HB, Feskens EJ, Kromhout D. Dietary catechins and epithelial cancer incidence: the Zutphen elderly study. Int J Cancer 2001; 92: 298–302. - PubMed
-
- Knekt P, Kumpulainen J, Järvinen R, Rissanen H, Heliövaara M, Reunanen A, Hakulinen T, Aromaa A. Flavonoid intake and risk of chronic diseases. Am J Clin Nutr 2002; 76: 560–8. - PubMed
-
- Le Marchand L, Murphy SP, Hankin JH, Wilkens LR, Kolonel LN. Intake of flavonoids and lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 2000; 92: 154–60. - PubMed
-
- Shen SC, Chen YC, Hsu FL, Lee WR. Differential apoptosis-inducing effect of quercetin and its glycosides in human promyeloleukemic HL-60 cells by alternative activation of the caspase 3 cascade. J Cell Biochem 2003; 89: 1044–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

