The role and regulation of IGFBP-1 phosphorylation in fetal growth restriction
- PMID: 25682045
- PMCID: PMC4458246
- DOI: 10.1007/s12079-015-0266-x
The role and regulation of IGFBP-1 phosphorylation in fetal growth restriction
Abstract
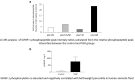
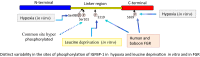
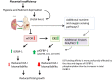
Fetal growth restriction (FGR) increases the risk of perinatal complications and predisposes the infant to developing metabolic, cardiovascular, and neurological diseases in childhood and adulthood. The pathophysiology underlying FGR remains poorly understood and there is no specific treatment available. Biomarkers for early detection are also lacking. The insulin-like growth factor (IGF) system is an important regulator of fetal growth. IGF-I is the primary regulator of fetal growth, and fetal circulating levels of IGF-I are decreased in FGR. IGF-I activity is influenced by a family of IGF binding proteins (IGFBPs), which bind to IGF-I and decrease its bioavailability. During fetal development the predominant IGF-I binding protein in fetal circulation is IGFBP-1, which is primarily secreted by the fetal liver. IGFBP-1 binds IGF-I and thereby inhibits its bioactivity. Fetal circulating levels of IGF-I are decreased and concentrations of IGFBP-1 are increased in FGR. Phosphorylation of human IGFBP-1 at specific sites markedly increases its binding affinity for IGF-I, further limiting IGF-I bioactivity. Recent experimental evidence suggests that IGFBP-1 phosphorylation is markedly increased in the circulation of FGR fetuses suggesting an important role of IGFBP-1 phosphorylation in the regulation of fetal growth. Understanding of the significance of site-specific IGFBP-1 phosphorylation and how it is regulated to contribute to fetal growth will be an important step in designing strategies for preventing, managing, and/or treating FGR. Furthermore, IGFBP-1 hyperphosphorylation at unique sites may serve as a valuable biomarker for FGR.
Figures

References
-
- Abu Shehab M, Inoue S, Han VK, Gupta MB. Site specific phosphorylation of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) for evaluating clinical relevancy in fetal growth restriction. J Proteome Res. 2009;8:5325–5335. - PubMed
-
- Abu Shehab M, Khosravi J, Han VK, Shilton BH, Gupta MB. Site-specific IGFBP-1 hyper-phosphorylation in fetal growth restriction: clinical and functional relevance. J Proteome Res. 2010;9:1873–1881. - PubMed
-
- Abu Shehab M, Iosef C, Wildgruber R, Sardana G, Gupta MB. Phosphorylation of IGFBP-1 at discrete sites elicits variable effects on IGF-I receptor autophosphorylation. Endocrinology. 2013;154:1130–1143. - PubMed
-
- Ankrapp DP, Jones JI, Clemmons DR. Characterization of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 kinases from human hepatoma cells. J Cell Biochem. 1996;60:387–399. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

