Methylation and microRNA-mediated epigenetic regulation of SOCS3
- PMID: 25682267
- PMCID: PMC5542822
- DOI: 10.1007/s11033-015-3860-3
Methylation and microRNA-mediated epigenetic regulation of SOCS3
Abstract
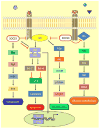
Epigenetic gene silencing of several genes causes different pathological conditions in humans, and DNA methylation has been identified as one of the key mechanisms that underlie this evolutionarily conserved phenomenon associated with developmental and pathological gene regulation. Recent advances in the miRNA technology with high throughput analysis of gene regulation further increased our understanding on the role of miRNAs regulating multiple gene expression. There is increasing evidence supporting that the miRNAs not only regulate gene expression but they also are involved in the hypermethylation of promoter sequences, which cumulatively contributes to the epigenetic gene silencing. Here, we critically evaluated the recent progress on the transcriptional regulation of an important suppressor protein that inhibits cytokine-mediated signaling, SOCS3, whose expression is directly regulated both by promoter methylation and also by microRNAs, affecting its vital cell regulating functions. SOCS3 was identified as a potent inhibitor of Jak/Stat signaling pathway which is frequently upregulated in several pathologies, including cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, viral infections, and the expression of SOCS3 was inhibited or greatly reduced due to hypermethylation of the CpG islands in its promoter region or suppression of its expression by different microRNAs. Additionally, we discuss key intracellular signaling pathways regulated by SOCS3 involving cellular events, including cell proliferation, cell growth, cell migration and apoptosis. Identification of the pathway intermediates as specific targets would not only aid in the development of novel therapeutic drugs, but, would also assist in developing new treatment strategies that could successfully be employed in combination therapy to target multiple signaling pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Down-regulation of hsa-miR-1264 contributes to DNMT1-mediated silencing of SOCS3.Mol Biol Rep. 2015 Sep;42(9):1365-76. doi: 10.1007/s11033-015-3882-x. Mol Biol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26047583 Free PMC article.
-
Methylation-associated dysregulation of the suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 gene in multiple myeloma.Epigenetics. 2011 Aug;6(8):1047-52. doi: 10.4161/epi.6.8.16167. Epub 2011 Aug 1. Epigenetics. 2011. PMID: 21934357
-
Methylation status of the SOCS3 gene in human malignant melanomas.Int J Oncol. 2007 Mar;30(3):689-94. Int J Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17273770
-
Epigenetic alterations in cholangiocarcinoma-sustained IL-6/STAT3 signaling in cholangio- carcinoma due to SOCS3 epigenetic silencing.Digestion. 2009;79 Suppl 1:2-8. doi: 10.1159/000167859. Epub 2009 Jan 20. Digestion. 2009. PMID: 19153483 Review.
-
Emerging roles of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 in human cancers.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Dec;144:112262. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112262. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34607102 Review.
Cited by
-
SOCS3, Transcriptionally Activated by NR4A1, Induces Apoptosis and Extracellular Matrix Degradation of Vaginal Fibroblasts in Pelvic Organ Prolapse.Balkan Med J. 2024 Mar 1;41(2):105-112. doi: 10.4274/balkanmedj.galenos.2023.2023-10-60. Epub 2024 Jan 17. Balkan Med J. 2024. PMID: 38229336 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Innate Immunity by microRNAs.Antibodies (Basel). 2016 Apr 1;5(2):8. doi: 10.3390/antib5020008. Antibodies (Basel). 2016. PMID: 31557989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tissue levels of suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 (SOCS-3) in mycosis fungoides.Arch Dermatol Res. 2023 Mar;315(2):165-171. doi: 10.1007/s00403-022-02339-x. Epub 2022 Feb 28. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023. PMID: 35226171 Free PMC article.
-
Short communication: TNF-α and IGF-1 regulates epigenetic mechanisms of HDAC2 and HDAC10.PLoS One. 2022 Feb 10;17(2):e0263190. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263190. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35143520 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of hsa-miR-1264 contributes to DNMT1-mediated silencing of SOCS3.Mol Biol Rep. 2015 Sep;42(9):1365-76. doi: 10.1007/s11033-015-3882-x. Mol Biol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26047583 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rhee I, Bachman KE, Park BH, Jair KW, Yen RW, Schuebel KE, Cui H, Feinberg AP, Lengauer C, Kinzler KW, Baylin SB, Vogelstein B. DNMT1 and DNMT3b cooperate to silence genes in human cancer cells. Nature. 2002;416:552–556. - PubMed
-
- Paz MF, Wei S, Cigudosa JC, Rodriguez-Perales S, Peinado MA, Huang TH, Esteller M. Genetic unmasking of epigenetically silenced tumor suppressor genes in colon cancer cells deficient in DNA methyltransferases. Hum Mol Genet. 2003;12:2209–2219. - PubMed
-
- Ballestar E, Esteller M. The epigenetic breakdown of cancer cells: from DNA methylation to histone modifications. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2005;38:169–181. - PubMed
-
- Lopez-Serra L, Ballestar E, Fraga MF, Alaminos M, Setien F, Esteller M. A profile of methyl-CpG binding domain protein occupancy of hypermethylated promoter CpG islands of tumor suppressor genes in human cancer. Cancer Res. 2006;66:8342–8346. - PubMed
-
- Robertson KD, Ait-Si-Ali S, Yokochi T, Wade PA, Jones PL, Wolffe AP. DNMT1 forms a complex with Rb, E2F1 and HDAC1 and represses transcription from E2F-responsive promoters. Nat Genet. 2000;25:338–342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

