Regulation of TWIK-related potassium channel-1 (Trek1) restitutes intestinal epithelial barrier function
- PMID: 25683610
- PMCID: PMC4711681
- DOI: 10.1038/cmi.2014.137
Regulation of TWIK-related potassium channel-1 (Trek1) restitutes intestinal epithelial barrier function
Abstract
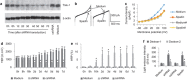
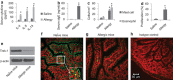
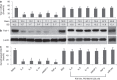
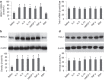
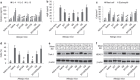
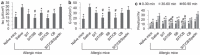
The disruption of epithelial barrier integrity is an important factor in the pathogenesis of various immune disorders. However, the restitution of the compromised barrier functions is difficult. This study investigates the regulation of TWIK-related potassium channel-1 (Trek1) in the restitution of intestinal epithelial barrier functions. The human colon epithelial cell line T84 was cultured in monolayers and used to observe epithelial barrier functions in vitro. An intestinal allergy mouse model was created. Cytokine levels were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and western blotting. The results showed that Trek1 deficiency induced T84 monolayer barrier disruption. Allergic responses markedly suppressed the expression of Trek1 in the intestinal epithelia via activating the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways and increasing the expression of histone deacetylase-1. The inhibition of histone deacetylase-1 by sodium butyrate or the administration of a butyrate-producing probiotic (Clostridium butyricum) restored the intestinal epithelial barrier functions and markedly enhanced the effect of antigen-specific immunotherapy. The data suggest that Trek1 is required for the maintenance of intestinal epithelial barrier integrity. Allergic responses induce an insufficiency of Trek1 expression in the intestinal epithelia. Trek1 expression facilitates the restoration of intestinal epithelial barrier functions in an allergic environment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of Trek1 expression in nasal mucosa with allergic rhinitis by specific immunotherapy.Cell Biochem Funct. 2015 Jan;33(1):23-8. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3075. Epub 2014 Dec 22. Cell Biochem Funct. 2015. PMID: 25529528
-
Trek1 contributes to maintaining nasal epithelial barrier integrity.Sci Rep. 2015 Mar 17;5:9191. doi: 10.1038/srep09191. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25778785 Free PMC article.
-
Specific immunotherapy in combination with Clostridium butyricum inhibits allergic inflammation in the mouse intestine.Sci Rep. 2015 Dec 2;5:17651. doi: 10.1038/srep17651. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26627845 Free PMC article.
-
TREK-king the blood-brain-barrier.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014 Jun;9(3):293-301. doi: 10.1007/s11481-014-9530-8. Epub 2014 Feb 21. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24557892 Review.
-
Cellular signaling in rapid intestinal epithelial restitution: implication of polyamines and K+ channels.Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2003 Aug 25;55(4):365-72. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2003. PMID: 12937813 Review.
Cited by
-
Update on the Pathogenesis of the Hirschsprung-Associated Enterocolitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 27;24(5):4602. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054602. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Negative Influence by the Force: Mechanically Induced Hyperpolarization via K2P Background Potassium Channels.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 23;22(16):9062. doi: 10.3390/ijms22169062. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ion channel regulation of gut immunity.J Gen Physiol. 2023 Feb 6;155(2):e202113042. doi: 10.1085/jgp.202113042. Epub 2022 Dec 2. J Gen Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36459135 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial-Derived Butyrate Promotes Epithelial Barrier Function through IL-10 Receptor-Dependent Repression of Claudin-2.J Immunol. 2017 Oct 15;199(8):2976-2984. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700105. Epub 2017 Sep 11. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28893958 Free PMC article.
-
Mast Cells in Gut and Brain and Their Potential Role as an Emerging Therapeutic Target for Neural Diseases.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Jul 30;13:345. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00345. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31417365 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- 2Fries W, Belvedere A, Vetrano S. Sealing the broken barrier in IBD: intestinal permeability, epithelial cells and junctions. Curr Drug Targets 2013; 14: 1460–1470. - PubMed
-
- 3Swindle EJ, Collins JE, Davies DE. Breakdown in epithelial barrier function in patients with asthma: identification of novel therapeutic approaches. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2009; 124: 23–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

