Microbes Promote Amino Acid Harvest to Rescue Undernutrition in Drosophila
- PMID: 25683709
- PMCID: PMC4534362
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.01.018
Microbes Promote Amino Acid Harvest to Rescue Undernutrition in Drosophila
Abstract
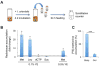
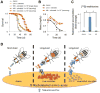
Microbes play an important role in the pathogenesis of nutritional disorders such as protein-specific malnutrition. However, the precise contribution of microbes to host energy balance during undernutrition is unclear. Here, we show that Issatchenkia orientalis, a fungal microbe isolated from field-caught Drosophila melanogaster, promotes amino acid harvest to rescue the lifespan of undernourished flies. Using radioisotope-labeled dietary components (amino acids, nucleotides, and sucrose) to quantify nutrient transfer from food to microbe to fly, we demonstrate that I. orientalis extracts amino acids directly from nutrient-poor diets and increases protein flux to the fly. This microbial association restores body mass, protein, glycerol, and ATP levels and phenocopies the metabolic profile of adequately fed flies. Our study uncovers amino acid harvest as a fundamental mechanism linking microbial and host metabolism, and highlights Drosophila as a platform for quantitative studies of host-microbe relationships.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
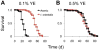

Similar articles
-
The Nutritional Environment Influences the Impact of Microbes on Drosophila melanogaster Life Span.mBio. 2019 Jul 9;10(4):e00885-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00885-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31289176 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial Quantity Impacts Drosophila Nutrition, Development, and Lifespan.iScience. 2018 Jun 29;4:247-259. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2018.06.004. Epub 2018 Jun 8. iScience. 2018. PMID: 30240744 Free PMC article.
-
The Increased Abundance of Commensal Microbes Decreases Drosophila melanogaster Lifespan through an Age-Related Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction.Insects. 2022 Feb 21;13(2):219. doi: 10.3390/insects13020219. Insects. 2022. PMID: 35206792 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila melanogaster in nutrition research-the importance of standardizing experimental diets.Genes Nutr. 2019 Feb 1;14:3. doi: 10.1186/s12263-019-0627-9. eCollection 2019. Genes Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30766617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interplay between intestinal bacteria and host metabolism in health and disease: lessons from Drosophila melanogaster.Dis Model Mech. 2016 Mar;9(3):271-81. doi: 10.1242/dmm.023408. Dis Model Mech. 2016. PMID: 26935105 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stable Host Gene Expression in the Gut of Adult Drosophila melanogaster with Different Bacterial Mono-Associations.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 29;11(11):e0167357. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167357. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27898741 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial and fungal components of the microbiome have distinct roles in Hawaiian drosophila reproduction.ISME Commun. 2024 Nov 4;4(1):ycae134. doi: 10.1093/ismeco/ycae134. eCollection 2024 Jan. ISME Commun. 2024. PMID: 39678232 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal commensal bacteria promote Bactrocera dorsalis larval development through the vitamin B6 synthesis pathway.Microbiome. 2024 Nov 4;12(1):227. doi: 10.1186/s40168-024-01931-9. Microbiome. 2024. PMID: 39491009 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Cooperation among Commensal Bacteria Supports Drosophila Juvenile Growth under Nutritional Stress.iScience. 2020 Jun 26;23(6):101232. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101232. Epub 2020 Jun 4. iScience. 2020. PMID: 32563155 Free PMC article.
-
Commensal bacteria and essential amino acids control food choice behavior and reproduction.PLoS Biol. 2017 Apr 25;15(4):e2000862. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2000862. eCollection 2017 Apr. PLoS Biol. 2017. PMID: 28441450 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alcazar EB, Rocha-Leao MHM, Dweck J. Yeast intracellular water determination by thermogravimetry. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2000;59:643–648.
-
- Anagnostou C, Dorsch M, Rohlfs M. Influence of dietary yeasts on Drosophila melanogaster life-history traits. Entomol Exp Et Appl. 2010;136:1–11.
-
- Ashburner M, Golic KG, Hawley SR. Parasites, pests, and diseases. In: Ashburner M, Golic KG, Hawley SR, editors. Drosophila: A laboratory handbook. New York: CSHL Press; 2005. pp. 1285–1332.
-
- Bakula M. Persistence of a microbial flora during postembryogenesis of Drosophila melanogaster. J Invertebr Pathol. 1969;14:365–374. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

