Selective spinal anesthesia using 1 mg of bupivacaine with opioid in elderly patients for transurethral resection of prostate
- PMID: 25684006
- PMCID: PMC4329369
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.2.535
Selective spinal anesthesia using 1 mg of bupivacaine with opioid in elderly patients for transurethral resection of prostate
Abstract
Purpose: This study was to evaluate the characteristics of selective spinal anesthesia using 1 mg of bupivacaine combined with fentanyl or sufentanil in elderly patients undergoing transurethral resection of prostate.
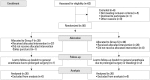
Materials and methods: Fifty-six patients were randomized into two groups. The Fentanyl group received 0.5% hyperbaric bupivacaine 0.2 mL+fentanyl 20 μg+5% dextrose 1.4 mL, and the Sufentanil group received 0.5% hyperbaric bupivacaine 0.2 mL+sufentanil 5 μg+5% dextrose 1.7 mL intrathecally. Intraoperative and postoperative characteristics were evaluated. Patient satisfaction was assessed postoperatively.
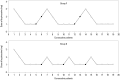
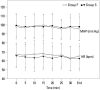
Results: Twenty-six patients in each group completed the study. The median peak sensory block level was similar between two groups, but sensory regression time was longer in the Sufentanil group than the Fentanyl group (p=0.017). All patients were able to move themselves to the bed without any aid when they arrived at the admission room. Pain scores were lower in the Sufentanil group than the Fentanyl group at postoperative 6, 12, and 18 hours (p=0.001). Compared to the Fentanyl group, the Sufentanil group required less postoperative analgesia (p=0.023) and the time to the first analgesic request was longer (p=0.025). Twenty-four of 26 patients (92.3%) in each group showed "good" satisfaction level.
Conclusion: Selective spinal anesthesia using 1 mg of bupivacaine with fentanyl or sufentanil provided appropriate sensory block level with spared motor function for transurethral resection of the prostate in elderly patients. Intrathecal sufentanil was superior to fentanyl in postoperative analgesic quality.
Keywords: 1 mg bupivacaine; Transurethral resection of prostate; aged patients; anesthesia; opioids; spinal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Arrighi HM, Metter EJ, Guess HA, Fozzard JL. Natural history of benign prostatic hyperplasia and risk of prostatectomy. The Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. Urology. 1991;38(1 Suppl):4–8. - PubMed
-
- Berry SJ, Coffey DS, Walsh PC, Ewing LL. The development of human benign prostatic hyperplasia with age. J Urol. 1984;132:474–479. - PubMed
-
- Li MK, Garcia L, Patron N, Moh LC, Sundram M, Leungwattanakij S, et al. An Asian multinational prospective observational registry of patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia, with a focus on comorbidities, lower urinary tract symptoms and sexual function. BJU Int. 2008;101:197–202. - PubMed
-
- Kim SY, Cho JE, Hong JY, Koo BN, Kim JM, Kil HK. Comparison of intrathecal fentanyl and sufentanil in low-dose dilute bupivacaine spinal anaesthesia for transurethral prostatectomy. Br J Anaesth. 2009;103:750–754. - PubMed
-
- Hong JY, Yang SC, Ahn S, Kil HK. Preoperative comorbidities and relationship of comorbidities with postoperative complications in patients undergoing transurethral prostate resection. J Urol. 2011;185:1374–1378. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

