Food security and sustainability: can one exist without the other?
- PMID: 25684016
- PMCID: PMC10271846
- DOI: 10.1017/S136898001500021X
Food security and sustainability: can one exist without the other?
Abstract
Objective: To position the concept of sustainability within the context of food security.
Design: An overview of the interrelationships between food security and sustainability based on a non-systematic literature review and informed discussions based principally on a quasi-historical approach from meetings and reports.
Setting: International and global food security and nutrition.
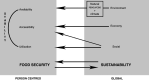
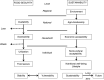
Results: The Rome Declaration on World Food Security in 1996 defined its three basic dimensions as: availability, accessibility and utilization, with a focus on nutritional well-being. It also stressed the importance of sustainable management of natural resources and the elimination of unsustainable patterns of food consumption and production. In 2009, at the World Summit on Food Security, the concept of stability/vulnerability was added as the short-term time indicator of the ability of food systems to withstand shocks, whether natural or man-made, as part of the Five Rome Principles for Sustainable Global Food Security. More recently, intergovernmental processes have emphasized the importance of sustainability to preserve the environment, natural resources and agro-ecosystems (and thus the overlying social system), as well as the importance of food security as part of sustainability and vice versa.
Conclusions: Sustainability should be considered as part of the long-term time dimension in the assessment of food security. From such a perspective the concept of sustainable diets can play a key role as a goal and a way of maintaining nutritional well-being and health, while ensuring the sustainability for future food security. Without integrating sustainability as an explicit (fifth?) dimension of food security, today's policies and programmes could become the very cause of increased food insecurity in the future.
Keywords: Food security and nutrition; Indicators; Nutritional well-being; Sustainability; Sustainable diets.
Figures
References
-
- Borlaug N (1970) Norman Borlaug’s Acceptance Speech, on the occasion of the award of the Nobel Peace Prize in Oslo, December 10, 1970. http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/peace/laureates/1970/borlaug-acce... (accessed December 2014).
-
- United Nations (1975) Report of the World Food Conference, Rome, 5–16 November 1974. New York: UN.
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (1996) Rome Declaration on Food Security and World Food Summit Plan of Action. Rome: FAO.
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (2009) Declaration of the World Food Summit on Food Security. Rome: FAO.
-
- United Nations (1987) Our Common Future. Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development. Geneva: UN.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical