Isoguanine and 5-methyl-isocytosine bases, in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 25684598
- PMCID: PMC4531829
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.201406392
Isoguanine and 5-methyl-isocytosine bases, in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
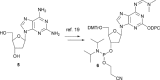
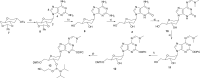
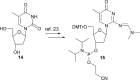
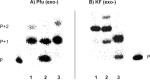
The synthesis, base-pairing properties and in vitro and in vivo characteristics of 5-methyl-isocytosine (isoC(Me) ) and isoguanine (isoG) nucleosides, incorporated in an HNA(h) (hexitol nucleic acid)-DNA(d) mosaic backbone, are described. The required h-isoG phosphoramidite was prepared by a selective deamination as a key step. As demonstrated by Tm measurements the hexitol sugar showed slightly better mismatch discrimination against dT. The d-isoG base mispairing follows the order T>G>C while the h-isoG base mispairing follows the order G>C>T. The h- and d-isoC(Me) bases mainly mispair with G. Enzymatic incorporation experiments show that the hexitol backbone has a variable effect on selectivity. In the enzymatic assays, isoG misincorporates mainly with T, and isoC(Me) misincorporates mainly with A. Further analysis in vivo confirmed the patterns of base-pair interpretation for the deoxyribose and hexitol isoC(Me) /isoG bases in a cellular context, through incorporation of the bases into plasmidic DNA. Results in vivo demonstrated that mispairing and misincorporation was dependent on the backbone scaffold of the base, which indicates rational advances towards orthogonality.
Keywords: HNA; XNA plasmid; isoG; nucleosides; polymerase.
© 2015 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures







References
-
- Herdewijn P, Marliere P. Chem. Biodiversity. 2009;6:791–808. - PubMed
-
- Pinheiro VB, Holliger P. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2012;16:245–252. - PubMed
-
- Chaput JC, Yu H, Zhang S. Chem. Biol. 2012;19:1360–1371. - PubMed
-
- Pochet S, Kaminski PA, Van Aerschot A, Herdewijn P, Marlière P. C. R. Biol. 2003;326:1175–1184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

