Urologist referral delay and its impact on survival after radical cystectomy for bladder cancer
- PMID: 25684993
- PMCID: PMC4324349
- DOI: 10.3747/co.22.2052
Urologist referral delay and its impact on survival after radical cystectomy for bladder cancer
Abstract
Background: Evidence shows that wait times before bladder cancer surgery have been increasing, and wait time can negatively affect survival. We aimed to determine if a long delay caused by an indirect referral before a first urologist visit affects the survival of patients undergoing radical cystectomy for bladder cancer.
Methods: We analyzed data from 1271 patients who underwent surgery for bladder cancer during the decade 2000-2009. The cohort was obtained by linking two administrative databases in the province of Quebec. Patients were considered to have been directly referred to a urologist if they had 5 or fewer visits with a general practitioner before their first urologist visit; otherwise, they were considered to have been indirectly referred. The effect on survival after surgery of a longer delay before a first urologist visit was assessed using Cox regression models.
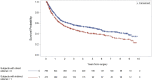
Results: Median referral delay for the study population was 30 days (56 days for women, 23 days for men; p < 0.0001). Indirect referral was observed for 49% of women and 33% of men. Compared with patients who were directly referred, those who were indirectly referred after first symptoms of bladder cancer experienced poorer survival (hazard ratio: 1.29; 95% confidence interval: 1.10 to 1.52). Women who were indirectly referred had a significant 47% greater risk of death after radical cystectomy. Men who were indirectly referred also experienced decreased survival (adjusted hazard ratio: 1.25; 95% confidence interval: 1.03 to 1.51).
Conclusions: Patients indirectly referred to a urologist had an increased risk of mortality after surgery. Compared with men, women had longer wait times and poorer survival.
Keywords: Urologist referral delay; bladder cancer; cohort study; radical cystectomy; survival.
Figures
References
-
- Canadian Cancer Society’s Advisory Committee on Cancer Statistics. Canadian Cancer Statistics 2013. Toronto, ON: Canadian Cancer Society; 2013.
-
- May M, Nitzke T, Helke C, Vogler H, Hoschke B. Significance of the time period between diagnosis of muscle invasion and radical cystectomy with regard to the prognosis of transitional cell carcinoma of the urothelium in the bladder. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 2004;38:231–5. doi: 10.1080/00365590410029141. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources