Interaction of graphene family materials with Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella enterica
- PMID: 25685114
- PMCID: PMC4312314
- DOI: 10.1186/s11671-015-0749-y
Interaction of graphene family materials with Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella enterica
Abstract
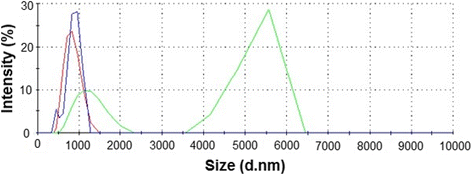
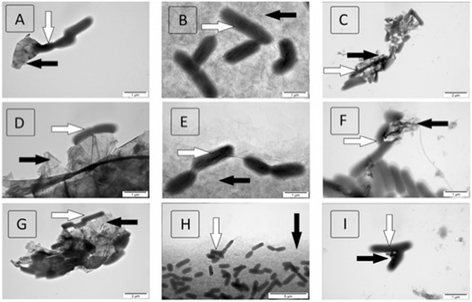
Graphene family materials have unique properties, which make them valuable for a range of applications. The antibacterial properties of graphene have been reported; however, findings have been contradictory. This study reports on the antimicrobial proprieties of three different graphene materials (pristine graphene (pG), graphene oxide (GO), and reduced graphene oxide (rGO)) against the food-borne bacterial pathogens Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella enterica. A high concentration (250 μg/mL) of all the analyzed graphenes completely inhibited the growth of both pathogens, despite their difference in bacterial cell wall structure. At a lower concentration (25 μg/mL), similar effects were only observed with GO, as growth inhibition decreased with pG and rGO at the lower concentration. Interaction of the nanoparticles with the pathogenic bacteria was found to differ depending on the form of graphene. Microscopic imaging demonstrated that bacteria were arranged at the edges of pG and rGO, while with GO, they adhered to the nanoparticle surface. GO was found to have the highest antibacterial activity.
Keywords: Bacteria growth; Graphene oxide; Listeria monocytogenes; Pristine graphene; Reduced graphene oxide; Salmonella enterica.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Oxidative stress-mediated antibacterial activity of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:5901-14. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S37397. Epub 2012 Nov 30. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 23226696 Free PMC article.
-
Viable-but-Nonculturable Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella enterica Serovar Thompson Induced by Chlorine Stress Remain Infectious.mBio. 2018 Apr 17;9(2):e00540-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00540-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 29666286 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical composition, antioxidant capacity and antibacterial action of five Moroccan essential oils against Listeria monocytogenes and different serotypes of Salmonella enterica.Microb Pathog. 2020 Dec;149:104510. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104510. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Microb Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32956790
-
Graphene-Based Materials for Inhibition of Wound Infection and Accelerating Wound Healing.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Feb;158:114184. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.114184. Epub 2022 Dec 30. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36587554 Review.
-
Applications of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide in advanced dental materials and therapies.J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2024 Feb 18;19(2):403-421. doi: 10.1016/j.jtumed.2024.02.002. eCollection 2024 Apr. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38405382 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis and Characterization of Silver and Graphene Nanocomposites and Their Antimicrobial and Photocatalytic Potentials.Molecules. 2022 Aug 15;27(16):5184. doi: 10.3390/molecules27165184. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36014424 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicity studies of six types of carbon nanoparticles in a chicken-embryo model.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017 Apr 7;12:2887-2898. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S131960. eCollection 2017. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 28435265 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered Nanomaterial Coatings for Food Packaging: Design, Manufacturing, Regulatory, and Sustainability Implications.Micromachines (Basel). 2024 Feb 6;15(2):245. doi: 10.3390/mi15020245. Micromachines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38398974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Graphene Oxide Exhibits Antifungal Activity against Bipolaris sorokiniana In Vitro and In Vivo.Microorganisms. 2022 Oct 9;10(10):1994. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10101994. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36296270 Free PMC article.
-
Graphene-based nanomaterials as antimicrobial surface coatings: A parallel approach to restrain the expansion of COVID-19.Surf Interfaces. 2021 Dec;27:101460. doi: 10.1016/j.surfin.2021.101460. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Surf Interfaces. 2021. PMID: 34957347 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sun W, Qi X, Zhang Y, Yang H, Gao H, Chen Y, et al. Electrochemical DNA biosensor for the detection of Listeria monocytogenes with dendritic nanogold and electrochemical reduced graphene modified carbon ionic liquid electrode. Electrochim Acta. 2012;85:145–51. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2012.07.133. - DOI
-
- Krishnamoorthy K. Antibacterial efficiency of graphene nanosheets against pathogenic bacteria via lipid peroxidation. J Phys Chem C. 2012;116:17280–7. doi: 10.1021/jp3047054. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

