The synergistic effects of heat shock protein 70 and ginsenoside Rg1 against tert-butyl hydroperoxide damage model in vitro
- PMID: 25685255
- PMCID: PMC4312651
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/437127
The synergistic effects of heat shock protein 70 and ginsenoside Rg1 against tert-butyl hydroperoxide damage model in vitro
Abstract
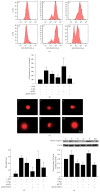
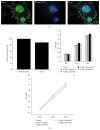
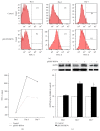
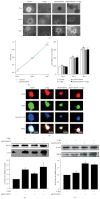
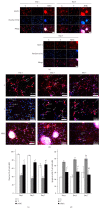
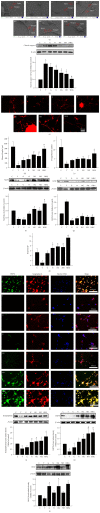
Neural stem cells (NSCs) transplanted is one of the hottest research to treat Alzheimer's disease (AD), but cholinergic neurons from stem cells were also susceptible to cell death which Heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) was affirmed to reverse. Related to cognitive impairment, cholinergic nervous cells should be investigated and ginsenoside Rg1 (G-Rg1) was considered to increase them. We chose tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BHP) damage model to study in vitro. Functional properties of our recombination plasmid pEGFP-C2-HSP70 were affirmed by SH-SY5Y cells. To opposite the transitory appearance of HSP70, NSCs used as the vectors of HSP70 gene overexpressed HSP70 for at least 7 days in vitro. After transfection for 3 days, G-Rg1 pretreatment for 4 hours, and coculture for 3 days, the expression of acetylcholinesterase (ChAT), synaptophysin, and the ratio of NeuN and GFAP were assessed by western blot; Morphological properties were detected by 3D reconstruction and immunofluorescence. ChAT was markedly improved in the groups contained G-Rg1. In coculture system, the ratio of neurons/astrocytes and the filaments of neurons were increased; apoptosis cells were decreased, compared to monotherapy (P < 0.05). In conclusion, we demonstrated that, as a safe cotreatment affirmed in vitro, overexpression of HSP70 in NSCs plus G-Rg1 promoted nervous cells regeneration from chronic oxidative damage.
Figures

References
-
- López Ó. L., DeKosky S. T. Neuropathology of Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment. Revista de Neurologia. 2003;37(2):155–163. - PubMed
-
- Zhang W., Wang P.-J., Sha H.-Y., Ni J., Li M.-H., Gu G.-J. Neural stem cell transplants improve cognitive function without altering amyloid pathology in an APP/PS1 double transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease. Molecular Neurobiology. 2014;50(2):423–437. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8640-x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Blurton-Jones M., Kitazawa M., Martinez-Coria H., et al. Neural stem cells improve cognition via BDNF in a transgenic model of Alzheimer disease. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2009;106(32):13594–13599. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0901402106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

