Implementation of an iPod wireless accelerometer application using machine learning to classify disparity of hemiplegic and healthy patellar tendon reflex pair
- PMID: 25685611
- PMCID: PMC4324531
- DOI: 10.1166/jmihi.2014.1219
Implementation of an iPod wireless accelerometer application using machine learning to classify disparity of hemiplegic and healthy patellar tendon reflex pair
Abstract
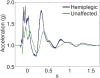
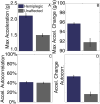
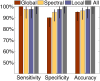
The characteristics of the patellar tendon reflex provide fundamental insight regarding the diagnosis of neurological status. Based on the features of the tendon reflex response, a clinician may establish preliminary perspective regarding the global condition of the nervous system. Current techniques for quantifying the observations of the reflex response involve the application of ordinal scales, requiring the expertise of a highly skilled clinician. However, the reliability of the ordinal scale approach is debatable. Highly skilled clinicians have even disputed the presence of asymmetric reflex pairs. An alternative strategy was the implementation of an iPod wireless accelerometer application to quantify the reflex response acceleration waveform. An application enabled the recording of the acceleration waveform and later wireless transmission as an email attachment by connectivity to the Internet. A potential energy impact pendulum enabled the patellar tendon reflex to be evoked in a predetermined and targeted manner. Three feature categories of the reflex response acceleration waveform (global parameters, temporal organization, and spectral features) were incorporated into machine learning to distinguish a subject's hemiplegic and healthy reflex pair. Machine learning attained perfect classification of the hemiplegic and healthy reflex pair. The research findings implicate the promise of machine learning for providing increased diagnostic acuity regarding the acceleration waveform of the tendon reflex response.
Figures

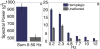
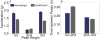
Similar articles
-
Quantified reflex strategy using an iPod as a wireless accelerometer application.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2012;2012:2476-9. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2012.6346466. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2012. PMID: 23366427
-
Implementation of an iPhone wireless accelerometer application for the quantification of reflex response.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2013;2013:4658-61. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2013.6610586. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2013. PMID: 24110773
-
Implementation of a smartphone as a wireless gyroscope application for the quantification of reflex response.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2014;2014:3654-7. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2014.6944415. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2014. PMID: 25570783
-
Wireless accelerometer reflex quantification system characterizing response and latency.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2009;2009:5283-6. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2009.5333086. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2009. PMID: 19963891
-
Contralateral influences on patellar tendon reflexes in young and old adults.Neurobiol Aging. 1989 Jul-Aug;10(4):311-5. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(89)90041-9. Neurobiol Aging. 1989. PMID: 2682314 Review.
References
-
- Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM. Principles of Neural Science. McGraw-Hill; New York: 2000.
-
- Bickley LS, Szilagyi PG. Bates' Guide to Physical Examination and History Taking. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; New York: 2003.
-
- LeMoyne R, Mastroianni T, Coroian C, Grundfest W. Tendon reflex and strategies for quantification, with novel methods incorporating wireless accelerometer reflex quantification devices, a perspective review. J Mech Med Biol. 2011;11:471–513.
-
- LeMoyne R. PhD dissertation. UCLA, Biomed. Eng. IDP; Los Angeles, CA: 2010. Wireless Quantified Reflex Device.
-
- Litvan I, Mangone CA, Werden W, Bueri JA, Estol CJ, Garcea DO, Rey RC, Sica RE, Hallett M, Bartko JJ. Reliabilityof the NINDS Myotatic Reflex Scale. Neurology. 1996;47:969–972. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
