White matter disruption at the prodromal stage of Alzheimer's disease: relationships with hippocampal atrophy and episodic memory performance
- PMID: 25685715
- PMCID: PMC4326466
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2015.01.014
White matter disruption at the prodromal stage of Alzheimer's disease: relationships with hippocampal atrophy and episodic memory performance
Abstract
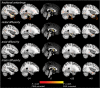
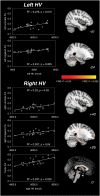
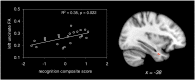
White matter tract alterations have been consistently described in Alzheimer's disease (AD). In particular, limbic fronto-temporal connections, which are critical to episodic memory function, may degenerate early in the course of the disease. However the relation between white matter tract degeneration, hippocampal atrophy and episodic memory impairment at the earliest stages of AD is still unclear. In this magnetic resonance imaging study, white matter integrity and hippocampal volumes were evaluated in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment due to AD (Albert et al., 2011) (n = 22) and healthy controls (n = 15). Performance in various episodic memory tasks was also evaluated in each participant. Relative to controls, patients showed a significant reduction of white matter fractional anisotropy (FA) and increase of radial diffusivity (RD) in the bilateral uncinate fasciculus, parahippocampal cingulum and fornix. Within the patient group, significant intra-hemispheric correlations were notably found between hippocampal grey matter volume and FA in the uncinate fasciculus, suggesting a relationship between atrophy and disconnection of the hippocampus. Moreover, episodic recognition scores were related with uncinate fasciculus FA across patients. These results indicate that fronto-hippocampal connectivity is reduced from the earliest pre-demential stages of AD. Disruption of fronto-hippocampal connections may occur progressively, in parallel with hippocampal atrophy, and may specifically contribute to early initial impairment in episodic memory.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Cingulum; Diffusion tensor imaging; Episodic memory; Prodromal AD; Uncinate fasciculus.
Figures

References
-
- Albert M.S., DeKosky S.T., Dickson D., Dubois B., Feldman H.H., Fox N.C., Gamst A., Holtzman D.M., Jagust W.J., Petersen R.C., Snyder P.J., Carrillo M.C., Thies B., Phelps C.H. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer's disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging–Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011;7(3):270–279. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

