An overview of the available methods for morphological scoring of pre-implantation embryos in in vitro fertilization
- PMID: 25685730
- PMCID: PMC4297478
- DOI: 10.22074/cellj.2015.486
An overview of the available methods for morphological scoring of pre-implantation embryos in in vitro fertilization
Abstract
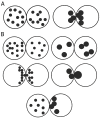
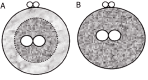
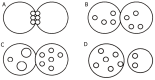
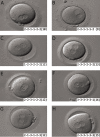
Assessment of embryo quality in order to choose the embryos that most likely result in pregnancy is the critical goal in assisted reproductive technologies (ART). The current trend in human in vitro fertilization/embryo transfer (IVF/ET) protocols is to decrease the rate of multiple pregnancies after multiple embryo transfer with maintaining the pregnancy rate at admissible levels (according to laboratory standards). Assessment of morphological feathers as a reliable non-invasive method that provides valuable information in prediction of IVF/intra cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) outcome has been frequently proposed in recent years. This article describes the current status of morphological embryo evaluation at different pre-implantation stages.
Keywords: Blastocyst; Cleavage Stage; Embryonic Development; In Vitro Fertilization; Zygote.
Figures

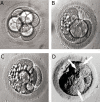
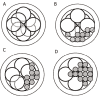
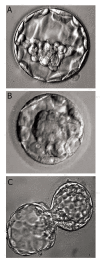
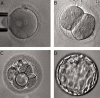
Similar articles
-
Guidelines for the number of embryos to transfer following in vitro fertilization No. 182, September 2006.Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2008 Aug;102(2):203-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ijgo.2008.01.007. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2008. PMID: 18773532 Review.
-
Value of the sperm deoxyribonucleic acid fragmentation level, as measured by the sperm chromatin dispersion test, in the outcome of in vitro fertilization and intracytoplasmic sperm injection.Fertil Steril. 2006 Feb;85(2):371-83. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2005.07.1327. Fertil Steril. 2006. PMID: 16595214
-
Paternal influence of sperm DNA integrity on early embryonic development.Hum Reprod. 2014 Nov;29(11):2402-12. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deu228. Epub 2014 Sep 8. Hum Reprod. 2014. PMID: 25205757
-
Oocyte insemination techniques are related to alterations of embryo developmental timing in an oocyte donation model.Reprod Biomed Online. 2013 Oct;27(4):367-75. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2013.06.017. Epub 2013 Jul 12. Reprod Biomed Online. 2013. PMID: 23953584
-
Avoiding multiple pregnancies in ART: a plea for single embryo transfer.Hum Reprod. 2000 Sep;15(9):1884-8. doi: 10.1093/humrep/15.9.1884. Hum Reprod. 2000. PMID: 10966980 Review.
Cited by
-
Urinary Organophosphate Metabolite Concentrations and Pregnancy Outcomes among Women Conceiving through in Vitro Fertilization in Shanghai, China.Environ Health Perspect. 2020 Sep;128(9):97007. doi: 10.1289/EHP7076. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Environ Health Perspect. 2020. PMID: 32997523 Free PMC article.
-
Association between sex and the developmental morphokinetics of in vitro derived bovine embryos.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 5;15(1):28631. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14017-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40764380 Free PMC article.
-
Body mass index, not race, may be associated with an alteration in early embryo morphokinetics during in vitro fertilization.J Assist Reprod Genet. 2021 Dec;38(12):3091-3098. doi: 10.1007/s10815-021-02350-7. Epub 2021 Nov 22. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2021. PMID: 34806132 Free PMC article.
-
Raman spectrum: A potential biomarker for embryo assessment during in vitro fertilization.Exp Ther Med. 2017 May;13(5):1789-1792. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4160. Epub 2017 Feb 23. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 28565768 Free PMC article.
-
The complex microbiome from native semen to embryo culture environment in human in vitro fertilization procedure.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2020 Jan 16;18(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12958-019-0562-z. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 31948459 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Depa-Martynow M, Jedrzejczak P, Pawelczyk L. Pronuclear scoring as a predictor of embryo quality in in vitro fertilization program. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2007;45(Suppl 1):S85–89. - PubMed
-
- Cummins JM, Breen TM, Harrison KL, Shaw JM, Wilson LM, Hennessey JF. A formula for scoring human embryo growth rates in in vitro fertilization: its value in predicting pregnancy and in comparison with visual estimates of embryo quality. J In Vitro Fert Embryo Transf. 1986;3(5):284–295. - PubMed
-
- Shoukir Y, Campana A, Farley T, Sakkas D. Early cleavage of in-vitro fertilized human embryos to the 2-cell stage: a novel indicator of embryo quality and viability. Hum Reprod. 1997;12(7):1531–1536. - PubMed
-
- Desai N, Goldstein J, Rowland DY, Goldfarb JM. Morphological evaluation of human embryos and derivation of an embryo quality scoring system specific for day 3 embryos: a preliminary. Hum Reprod. 2000;15(10):2190–2196. - PubMed
-
- Ziebe S, Petersen K, Lindenberg S, Andersen AG, Gabrielsen A, Andersen AN. Embryo morphology or cleavage stage: how to select the best embryos for transfer after in-vitro fertilization. Hum Reprod. 1997;12(7):1545–1549. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
