Sweet syndrome and differentiation syndrome in a patient with acute promyelocytic leukemia
- PMID: 25685768
- PMCID: PMC4317615
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v3.i2.196
Sweet syndrome and differentiation syndrome in a patient with acute promyelocytic leukemia
Abstract
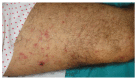
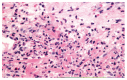
The differentiation syndrome is an inflammatory reaction with increased capillary permeability that occurs in up to 25% of patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia treated with all-trans retinoic acid. A 50-year-old man with acute promyelocytic leukemia underwent chemotherapy with idarubicin and all-trans retinoic acid. On day +21 the patient developed pruritic prepatelar papules as well as several 10 mm subcutaneous nodules in both thighs accompanied by persistent fever. On the day +25 the patient presented with bilateral pulmonary crackles, infiltrates in the right lower lobe and severe hypotension which required dopamine infusion. Biopsy of one of the thighs nodules was performed. A Sweet syndrome associated to a differentiation syndrome was suspected. All-trans retinoic acid therapy was discontinued and dexamethasone was administered. In 48 h the patient showed remission of the fever and the infiltrates and the skin lesions acquired a residual aspect. It is debatable whether these two syndromes are distinct entities with common mechanisms or whether they are poles of the same spectrum. Dermatologists and hematologists must be aware of these two syndromes and its pathophysiologic association.
Keywords: Acute promyelocytic leukemia; All-trans retinoic acid; Differentiation syndrome; Sweet syndrome.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The "retinoic acid syndrome" in acute promyelocytic leukemia.Ann Intern Med. 1992 Aug 15;117(4):292-6. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-117-4-292. Ann Intern Med. 1992. PMID: 1637024
-
Sweet Syndrome in an Adolescent Patient With Differentiation Syndrome Secondary to Promyelocytic Leukemia Treatment With All-Trans Retinoic Acid.J Med Cases. 2021 Dec;12(12):469-473. doi: 10.14740/jmc3758. Epub 2021 Dec 2. J Med Cases. 2021. PMID: 34970368 Free PMC article.
-
Sweet's syndrome during treatment with all-trans retinoic acid in a patient with acute promyelocytic leukemia.Leuk Lymphoma. 1998 Nov;31(5-6):613-5. doi: 10.3109/10428199809057622. Leuk Lymphoma. 1998. PMID: 9922053
-
Sweet's syndrome involoving the musculoskeletal system during treatment of promyelocytic leukemia with all-trans retinoic acid.Leukemia. 1996 Apr;10(4):731-4. Leukemia. 1996. PMID: 8618455 Review.
-
Sweet's syndrome in a patient with acute promyelocytic leukemia during treatment with all-trans retinoic acid.Int J Hematol. 1995 Oct;62(3):183-7. doi: 10.1016/0925-5710(95)00403-f. Int J Hematol. 1995. PMID: 8589363 Review.
Cited by
-
Midostaurin-induced Sweet syndrome in a patient with FLT3-ITD-positive AML.BMJ Case Rep. 2021 Aug 20;14(8):e243615. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2021-243615. BMJ Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34417240 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Astudillo L, Loche F, Reynish W, Rigal-Huguet F, Lamant L, Pris J. Sweet’s syndrome associated with retinoic acid syndrome in a patient with promyelocytic leukemia. Ann Hematol. 2002;81:111–114. - PubMed
-
- Astudillo L, Sailler L, Launay F, Josse AG, Lamant L, Couret B, Arlet-Suau E. Pulmonary involvement in Sweet’s syndrome: a case report and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2006;45:677–680. - PubMed
-
- Takada S, Matumoto K, Sakura T, Shiozaki H, Miyawaki S. Sweet’s syndrome followed by retinoic acid syndrome during the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with all-trans retinoic acid. Int J Hematol. 1999;70:26–29. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources