The versatile functions of Sox9 in development, stem cells, and human diseases
- PMID: 25685828
- PMCID: PMC4326072
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2014.09.004
The versatile functions of Sox9 in development, stem cells, and human diseases
Abstract
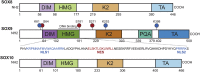
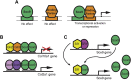
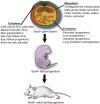
The transcription factor Sox9 was first discovered in patients with campomelic dysplasia, a haploinsufficiency disorder with skeletal deformities caused by dysregulation of Sox9 expression during chondrogenesis. Since then, its role as a cell fate determiner during embryonic development has been well characterized; Sox9 expression differentiates cells derived from all three germ layers into a large variety of specialized tissues and organs. However, recent data has shown that ectoderm- and endoderm-derived tissues continue to express Sox9 in mature organs and stem cell pools, suggesting its role in cell maintenance and specification during adult life. The versatility of Sox9 may be explained by a combination of post-transcriptional modifications, binding partners, and the tissue type in which it is expressed. Considering its importance during both development and adult life, it follows that dysregulation of Sox9 has been implicated in various congenital and acquired diseases, including fibrosis and cancer. This review provides a summary of the various roles of Sox9 in cell fate specification, stem cell biology, and related human diseases. Ultimately, understanding the mechanisms that regulate Sox9 will be crucial for developing effective therapies to treat disease caused by stem cell dysregulation or even reverse organ damage.
Keywords: Development; Diseases; Sox9; Stem cells; Transcription factor.
Figures

References
-
- Simons B.D., Clevers H. Stem cell self-renewal in intestinal crypt. Exp Cell Res. Nov 15 2011;317:2719–2724. - PubMed
-
- Rezza A., Sennett R., Rendl M. Adult stem cell niches: cellular and molecular components. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2014;107:333–372. - PubMed
-
- Gubbay J., Koopman P., Collignon J., Burgoyne P., Lovell-Badge R. Normal structure and expression of Zfy genes in XY female mice mutant in Tdy. Development. Jul 1990;109:647–653. - PubMed
-
- Sinclair A.H., Berta P., Palmer M.S. A gene from the human sex-determining region encodes a protein with homology to a conserved DNA-binding motif. Nature. Jul 19 1990;346:240–244. - PubMed
-
- Phochanukul N., Russell S. No backbone but lots of Sox: Invertebrate Sox genes. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. Mar 2010;42:453–464. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
