Valsartan Attenuates Atherosclerosis via Upregulating the Th2 Immune Response in Prolonged Angiotensin II-Treated ApoE(-/-) Mice
- PMID: 25685964
- PMCID: PMC4461573
- DOI: 10.2119/molmed.2014.00195
Valsartan Attenuates Atherosclerosis via Upregulating the Th2 Immune Response in Prolonged Angiotensin II-Treated ApoE(-/-) Mice
Abstract
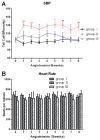
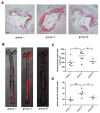
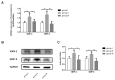
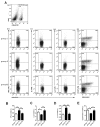
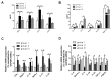
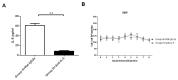
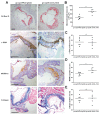
Valsartan has a protective effect against hypertension and atherosclerosis in humans and experimental animal models. This study aimed to determine the effect of prolonged treatment with angiotensin II (Ang II) on atherosclerosis and the effect of valsartan on the activity of CD4(+) T lymphocyte subsets. The results showed that prolonged treatment (8 wks) with exogenous Ang II resulted in an increased atherosclerotic plaque size and a switch of stable-to-unstable plaque via modulating on CD4(+) T lymphocyte activity, including an increase in the T helper cell type 1 (Th1) and Th17 cells and a decrease in Th2 and regulatory T (Treg) cells. In contrast, valsartan treatment efficiently reversed the imbalance in CD4(+) T lymphocyte activity, ameliorated atherosclerosis and elicited a stable plaque phenotype in addition to controlling blood pressure. In addition, treatment with anti-interleukin (IL)-5 monoclonal antibodies weakened the antiatherosclerotic effects of valsartan without affecting blood pressure.
Figures

References
-
- Robertson AK, Hansson GK. T cells in atherogenesis: for better or for worse? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:2421–32. - PubMed
-
- Frostegård J, et al. Cytokine expression in advanced human atherosclerotic plaques: dominance of pro-inflammatory (Th1) and macrophage-stimulating cytokines. Atherosclerosis. 1999;145:33–43. - PubMed
-
- Mazzolai L, et al. Endogenous angiotensin II induces atherosclerotic plaque vulnerability and elicits a Th1 response in ApoE−/− mice. Hypertension. 2004;44:277–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

