Photoaffinity labeling in target- and binding-site identification
- PMID: 25686004
- PMCID: PMC4413435
- DOI: 10.4155/fmc.14.152
Photoaffinity labeling in target- and binding-site identification
Abstract
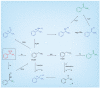
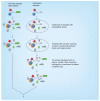
Photoaffinity labeling (PAL) using a chemical probe to covalently bind its target in response to activation by light has become a frequently used tool in drug discovery for identifying new drug targets and molecular interactions, and for probing the location and structure of binding sites. Methods to identify the specific target proteins of hit molecules from phenotypic screens are highly valuable in early drug discovery. In this review, we summarize the principles of PAL including probe design and experimental techniques for in vitro and live cell investigations. We emphasize the need to optimize and validate probes and highlight examples of the successful application of PAL across multiple disease areas.
Figures



References
-
- Lapinsky DJ. Tandem photoaffinity labeling-bioorthogonal conjugation in medicinal chemistry. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012;20:6237–6247. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto M, Hatanaka Y. Recent progress in diazirine-based photoaffinity labeling. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2008;15:2513–2523.
-
- Sadakane Y, Hatanaka Y. Photochemical fishing approaches for identifying target proteins and elucidating the structure of a ligand-binding region using carbene-generated photoreactive probes. Anal. Sci. 2006;22:209–218. - PubMed
-
- Singh A, Thornton ER, Westheimer FH. The photolysis of diazoacetylchymotrypsin. J. Biochem. 1962;237:3006–3008. - PubMed
-
- Das J. Aliphatic diazirines as photoaffinity probes for proteins: recent developments. Chem. Rev. 2011;111:4405–4417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
