Bibliometric trends in ophthalmology 1997-2009
- PMID: 25686064
- PMCID: PMC4363959
- DOI: 10.4103/0301-4738.151471
Bibliometric trends in ophthalmology 1997-2009
Abstract
Aims: To track citation patterns in ophthalmic journals and contrast them with major medical and surgical journals from 1997 to 2009. In addition, we want to familiarize the ophthalmic community with bibliometrics indices.
Materials and methods: Data retrieved from Institute for Scientific Information and related websites include 2-year journal impact factor JIF, 5-year impact, Eigenfactor score, H-factor, Article Influence score, and SCImago factor.
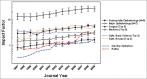
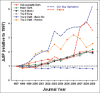
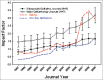
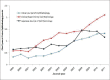
Results: JIF rose steadily around 10% annually in ophthalmic journals, and likewise for major medical and surgical journals. JIF correlated with recent bibliometric indicators like 5-year impact, H index, and SCImago factor but not with Eigenfactor. Ophthalmic journals publishing reviews, basic science, or large volume on broad range of topics ranked at the top for JIF, while subspecialty journals tended to have low JIF. JIF of subspecialty journal Retina rose from 0.740 (rank 23) in 2000 to 3.088 in 2007 (rank 6).
Conclusions: JIF tends to rise annually by 10% in medical, surgical, and ophthalmic fields. Journals publishing reviews, basic science, or large volume on broad range of topics rank at the top for JIF. The rapid rise of JIF for Retina unlike other subspecialties that stayed status quo is multifactorial: Change in editorial policies (introduction of review articles and omission of case reports) and technological advances in the retinal field.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of the h-indices of the editorial board members of seven ophthalmic subspecialty journals.J Fr Ophtalmol. 2019 Apr;42(4):349-353. doi: 10.1016/j.jfo.2018.10.008. Epub 2019 Mar 21. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2019. PMID: 30905439
-
Integrity of the editing and publishing process is the basis for improving an academic journal's Impact Factor.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Nov 21;28(43):6168-6202. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i43.6168. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36483155 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of scientometric data and publication policies of ophthalmology journals.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2022 May;70(5):1801-1807. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_2720_21. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35502077 Free PMC article.
-
Subspecialization of the ophthalmic literature: a review of the publishing trends of the top general, clinical ophthalmic journals.Ophthalmology. 2011 Jun;118(6):1211-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2010.10.023. Epub 2011 Jan 26. Ophthalmology. 2011. PMID: 21269704 Review.
-
Ophthalmology and vision science research. Part 1: Understanding and using journal impact factors and citation indices.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005 Oct;31(10):1999-2007. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2005.10.031. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005. PMID: 16338574 Review.
Cited by
-
Hotspots and trends in ophthalmology in recent 5 years: Bibliometric analysis in 2017-2021.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 26;9:988133. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.988133. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36091704 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in bibliometric indexes of the main dermatology journals (2009 to 2019).J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021 Sep;85(3):782-783. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.08.102. Epub 2020 Aug 29. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 32866551 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Emerging trends and frontier research on recurrent implantation failure: a bibliometric analysis.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Mar;10(6):307. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-703. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35433979 Free PMC article.
-
Worldwide ophthalmological research production 2000-2020, with special focus on the Nordic contribution.Acta Ophthalmol. 2022 Dec;100(8):e1760-e1766. doi: 10.1111/aos.15200. Epub 2022 Jun 7. Acta Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35670375 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in ophthalmology journals: a five-year bibliometric analysis (2009-2013).Int J Ophthalmol. 2016 Nov 18;9(11):1669-1675. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2016.11.22. eCollection 2016. Int J Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 27990374 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Simons K. The misused impact factor (Editorial) Science. 2008;322:165. - PubMed
-
- Garfield E. The history and meaning of the journal impact factors. JAMA. 2006;295:90–3. - PubMed
-
- McGhee CN. Analysis of New Zealand's research productivity in ophthalmology and vision science: 1993-2002. Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology: A decade of successful evolution. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2010;38:541–4. - PubMed
-
- Chou CY, Chew SS, Patel DV, Ormonde SE, McGhee CN. Publication and citation analysis of the Australian and New Zealand Journal of Ophthalmology and Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology over a 10-year period: The evolution of an ophthalmology journal. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2009;37:868–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

