Multilayered Nanoparticles for Gene Delivery Used to Reprogram Human Foreskin Fibroblasts to Neurospheres
- PMID: 25687130
- PMCID: PMC4523045
- DOI: 10.1089/ten.TEC.2014.0482
Multilayered Nanoparticles for Gene Delivery Used to Reprogram Human Foreskin Fibroblasts to Neurospheres
Abstract
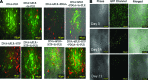
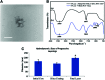
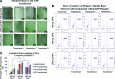
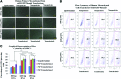
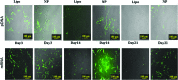
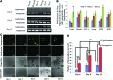
Polycationic nanocomplexes are a robust means for achieving nucleic acid condensation and efficient intracellular gene deliveries. To enhance delivery, a multilayered nanoparticle consisting of a core of electrostatically bound elements was used. These included a histone-mimetic peptides, poly-l-arginine and poly-d-glutamic acid was coated with silicate before surface functionalization with poly-l-arginine. Transfection efficiencies and duration of expression were similar when using green fluorescent protein (GFP) plasmid DNA (pDNA) or GFP mRNA. These nanoparticles demonstrated significantly higher (>100%) and significantly longer (15 vs. 4 days) transfection efficiencies in comparison to a commercial transfection agent (Lipofectamine 2000). Reprogramming of human foreskin fibroblasts using mRNA to the Sox2 transcription factor resulted in three-fold higher neurosphere formation in comparison to the commercial reagent. These results demonstrate the potential of these nanoparticles as ideal vectors for gene delivery.
Figures
References
-
- Musick M.A., McConnell K.I., Lue J.K., Wei F., Chen C., and Suh J. Reprogramming virus nanoparticles to bind metal ions upon activation with heat. Biomacromolecules 12, 2153, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Li H., Park S.H., Reif J.H., LaBean T.H., and Yan H. DNA-templated self-assembly of protein and nanoparticle linear arrays. J Am Chem Soc 126, 418, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Huangfu D., Osafune K., Maehr R., Guo W., Eijkelenboom A., Chen S., Muhlestein W., and Melton D.A. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from primary human fibroblasts with only Oct4 and Sox2. Nat Biotechnol 26, 1269, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

