Efficacy and safety of alirocumab in high cardiovascular risk patients with inadequately controlled hypercholesterolaemia on maximally tolerated doses of statins: the ODYSSEY COMBO II randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 25687353
- PMCID: PMC4430683
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv028
Efficacy and safety of alirocumab in high cardiovascular risk patients with inadequately controlled hypercholesterolaemia on maximally tolerated doses of statins: the ODYSSEY COMBO II randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Aims: To compare the efficacy [low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) lowering] and safety of alirocumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody to proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin 9, compared with ezetimibe, as add-on therapy to maximally tolerated statin therapy in high cardiovascular risk patients with inadequately controlled hypercholesterolaemia.
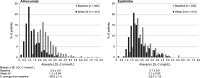
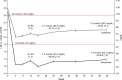
Methods and results: COMBO II is a double-blind, double-dummy, active-controlled, parallel-group, 104-week study of alirocumab vs. ezetimibe. Patients (n = 720) with high cardiovascular risk and elevated LDL-C despite maximal doses of statins were enrolled (August 2012-May 2013). This pre-specified analysis was conducted after the last patient completed 52 weeks. Patients were randomized to subcutaneous alirocumab 75 mg every 2 weeks (plus oral placebo) or oral ezetimibe 10 mg daily (plus subcutaneous placebo) on a background of statin therapy. At Week 24, mean ± SE reductions in LDL-C from baseline were 50.6 ± 1.4% for alirocumab vs. 20.7 ± 1.9% for ezetimibe (difference 29.8 ± 2.3%; P < 0.0001); 77.0% of alirocumab and 45.6% of ezetimibe patients achieved LDL-C <1.8 mmol/L (P < 0.0001). Mean achieved LDL-C at Week 24 was 1.3 ± 0.04 mmol/L with alirocumab and 2.1 ± 0.05 mmol/L with ezetimibe, and were maintained to Week 52. Alirocumab was generally well tolerated, with no evidence of an excess of treatment-emergent adverse events.
Conclusion: In patients at high cardiovascular risk with inadequately controlled LDL-C, alirocumab achieved significantly greater reductions in LDL-C compared with ezetimibe, with a similar safety profile.
Trial registration: clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: NCT01644188.
Keywords: Alirocumab; Ezetimibe; Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol; Monoclonal antibody.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Sweetless'n low LDL-C targets for PCSK9 treatment.Eur Heart J. 2015 May 14;36(19):1146-8. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv056. Epub 2015 Mar 31. Eur Heart J. 2015. PMID: 25827601 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cholesterol Treatment Trialists C Mihaylova B, Emberson J, Blackwell L, Keech A, Simes J, Barnes EH, Voysey M, Gray A, Collins R, Baigent C. The effects of lowering LDL cholesterol with statin therapy in people at low risk of vascular disease: meta-analysis of individual data from 27 randomised trials. Lancet 2012;380:581–590. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cholesterol Treatment Trialists (CTT) Collaboration Baigent C, Blackwell L, Emberson J, Holland LE, Reith C, Bhala N, Peto R, Barnes EH, Keech A, Simes J, Collins R. Efficacy and safety of more intensive lowering of LDL cholesterol: a meta-analysis of data from 170,000 participants in 26 randomised trials. Lancet 2010;376:1670–1681. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Perk J, De Backer G, Gohlke H, Graham I, Reiner Z, Verschuren M, Albus C, Benlian P, Boysen G, Cifkova R, Deaton C, Ebrahim S, Fisher M, Germano G, Hobbs R, Hoes A, Karadeniz S, Mezzani A, Prescott E, Ryden L, Scherer M, Syvanne M, Scholte op Reimer WJ, Vrints C, Wood D, Zamorano JL, Zannad F. European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice (version 2012). The Fifth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and Other Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice (constituted by representatives of nine societies and by invited experts). Developed with the special contribution of the European Association for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation (EACPR). Eur Heart J 2012;33:1635–1701. - PubMed
-
- Reiner Z, Catapano AL, De Backer G, Graham I, Taskinen MR, Wiklund O, Agewall S, Alegria E, Chapman MJ, Durrington P, Erdine S, Halcox J, Hobbs R, Kjekshus J, Filardi PP, Riccardi G, Storey RF, Wood D. ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: the Task Force for the management of dyslipidaemias of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS). Eur Heart J 2011;32:1769–1818. - PubMed
-
- Expert Panel on Detection Evaluation and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Executive Summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, And Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 2001;285:2486–2497. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

