Quantitative protein topography analysis and high-resolution structure prediction using hydroxyl radical labeling and tandem-ion mass spectrometry (MS)
- PMID: 25687570
- PMCID: PMC4390260
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.O114.044362
Quantitative protein topography analysis and high-resolution structure prediction using hydroxyl radical labeling and tandem-ion mass spectrometry (MS)
Abstract
Hydroxyl radical footprinting based MS for protein structure assessment has the goal of understanding ligand induced conformational changes and macromolecular interactions, for example, protein tertiary and quaternary structure, but the structural resolution provided by typical peptide-level quantification is limiting. In this work, we present experimental strategies using tandem-MS fragmentation to increase the spatial resolution of the technique to the single residue level to provide a high precision tool for molecular biophysics research. Overall, in this study we demonstrated an eightfold increase in structural resolution compared with peptide level assessments. In addition, to provide a quantitative analysis of residue based solvent accessibility and protein topography as a basis for high-resolution structure prediction; we illustrate strategies of data transformation using the relative reactivity of side chains as a normalization strategy and predict side-chain surface area from the footprinting data. We tested the methods by examination of Ca(+2)-calmodulin showing highly significant correlations between surface area and side-chain contact predictions for individual side chains and the crystal structure. Tandem ion based hydroxyl radical footprinting-MS provides quantitative high-resolution protein topology information in solution that can fill existing gaps in structure determination for large proteins and macromolecular complexes.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
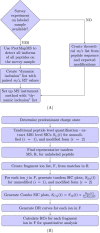
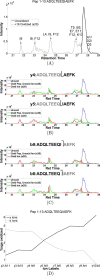
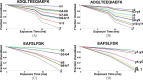

References
-
- Brenowitz M., Chance M. R., Dhavan G., Takamoto K. (2002) Probing the structural dynamics of nucleic acids by quantitative time-resolved and equilibrium hydroxyl radical “footprinting.” Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 12, 648–653 - PubMed
-
- Sclavi B., Sullivan M., Chance M. R., Brenowitz M., Woodson S. A. (1998) RNA folding at millisecond intervals by synchrotron hydroxyl radical footprinting. Science 279, 1940–1943 - PubMed
-
- Takamoto K., He Q., Morris S., Chance M. R., Brenowitz M. (2002) Monovalent cations mediate formation of native tertiary structure of the Tetrahymena thermophila ribozyme. Nat. Struct. Biol. 9, 928–933 - PubMed
-
- Shcherbakova I., Gupta S., Chance M. R., Brenowitz M. (2004) Monovalent ion-mediated folding of the Tetrahymena thermophila ribozyme. J. Mol. Biol. 342, 1431–1442 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

