Predicting pulmonary hypertension with standard computed tomography pulmonary angiography
- PMID: 25687575
- PMCID: PMC4428842
- DOI: 10.1007/s10554-015-0618-x
Predicting pulmonary hypertension with standard computed tomography pulmonary angiography
Abstract
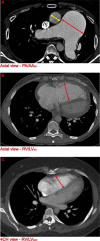
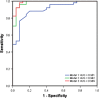
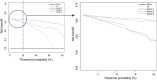
The most common feature of pulmonary hypertension (PH) on computed tomography pulmonary angiography (CTPA) is an increased diameter-ratio of the pulmonary artery to the ascending aorta (PA/AAAX). The aim of this study was to investigate whether combining PA/AAAX measurements with ventricular measurements improves the predictive value of CTPA for precapillary PH. Three predicting models were analysed using baseline CTPA scans of 51 treatment naïve precapillary PH patients and 25 non-PH controls: model 1: PA/AAAX only; model 2: PA/AAAX combined with the ratio of the right ventricular and left ventricular diameter measured on the axial view (RV/LVAX); model 3: PA/AAAX combined with the RV/LV-ratio measured on a four chamber view (RV/LV4CH). Prediction models were compared using multivariable binary logistic regression, ROC analyses and decision curve analyses (DCA). Multivariable binary logistic regression showed an improvement of the predictive value of model 2 (-2LL = 26.48) and 3 (-2LL = 21.03) compared to model 1 (-2LL = 21.03). ROC analyses showed significantly higher AUCs of model 2 and 3 compared to model 1 (p = 0.011 and p = 0.007, respectively). DCA showed an increased clinical benefit of model 2 and 3 compared to model 1. The predictive value of model 2 and 3 were almost equal. We found an optimal cut-off value for the RV/LV-ratio for predicting precapillary PH of RV/LV ≥ 1.20. The predictive value of CTPA for precapillary PH improves when ventricular and pulmonary artery measurements are combined. A PA/AAAX ≥ 1 or a RV/LVAX ≥ 1.20 needs further diagnostic evaluation to rule out or confirm the diagnosis.
Figures
References
-
- Galie N, Hoeper MM, Humbert M, Torbicki A, Vachiery JL, Barbera JA, Beghetti M, Corris P, Gaine S, Gibbs JS, Gomez-Sanchez MA, Jondeau G, Klepetko W, Opitz C, Peacock A, Rubin L, Zellweger M, Simonneau G. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J. 2009;34:1219–12163. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00139009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ling Y, Johnson MK, Kiely DG, Condliffe R, Elliot CA, Gibbs JS, Howard LS, Pepke-Zaba J, Sheares KK, Corris PA, Fisher AJ, Lordan JL, Gaine S, Coghlan JG, Wort SJ, Gatzoulis MA, Peacock AJ. Changing demographics, epidemiology, and survival of incident pulmonary arterial hypertension: results from the pulmonary hypertension registry of the United Kingdom and Ireland. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;186:790–796. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201203-0383OC. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Badesch DB, Raskob GE, Elliott CG, Krichman AM, Farber HW, Frost AE, Barst RJ, Benza RL, Liou TG, Turner M, Giles S, Feldkircher K, Miller DP, McGoon MD. Pulmonary arterial hypertension: baseline characteristics from the REVEAL Registry. Chest. 2010;137:376–387. doi: 10.1378/chest.09-1140. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

