Pemetrexed Singlet Versus Nonpemetrexed-Based Platinum Doublet as Second-Line Chemotherapy after First-Line Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Failure in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with EGFR Mutations
- PMID: 25687850
- PMCID: PMC4614214
- DOI: 10.4143/crt.2014.244
Pemetrexed Singlet Versus Nonpemetrexed-Based Platinum Doublet as Second-Line Chemotherapy after First-Line Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Failure in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with EGFR Mutations
Abstract
Purpose: Platinum-based doublet chemotherapy is the treatment of choice for patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); however, the role of a platinum-based doublet as second-line therapy after failure of an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) for NSCLC patients has not yet been elucidated. The purpose of this study was to compare the clinical efficacy of pemetrexed versus a platinum-based doublet as second-line therapy after failure of EGFR TKI used as first-line therapy for NSCLC patients with EGFR mutations.
Materials and methods: We designed a multicenter retrospective cohort study of 314 NSCLC patients with EGFR mutations who received an EGFR TKI as first-line palliative chemotherapy. Our analysis included 83 patients who failed EGFR TKI therapy and received second-line cytotoxic chemotherapy.
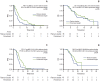
Results: Forty-six patients were treated using a platinum-based doublet and 37 patients were treated using singlet pemetrexed. The overall response rates of patients receiving a platinum-based doublet and patients receiving pemetrexed were17.4% and 32.4%, respectively (p=0.111). The median progression-free survival (PFS) of patients receiving pemetrexed was significantly longer than that of patients receiving a platinum-based doublet (4.2 months vs. 2.7 months, respectively; p=0.008). The hazard ratio was 0.54 (95% confidence interval, 0.34 to 0.86; p=0.009).
Conclusion: Our retrospective analysis found that second-line pemetrexed singlet therapy provided significantly prolonged PFS compared to second-line platinum-based doublet chemotherapy for NSCLC patients with EGFR mutations who failed first-line EGFR TKI. Conduct of prospective studies for confirmation of our results is warranted.
Keywords: Epidermal growth factor receptor; Non-small-cell lung carcinoma; Pemetrexed; Platinum.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest relevant to this article was not reported.
Figures

References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:10–29. - PubMed
-
- Novello S, Le Chevalier T. Chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer. Part 1: early-stage disease. Oncology (Williston Park) 2003;17:357–64. - PubMed
-
- Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP, Langer C, Sandler A, Krook J, et al. Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:92–8. - PubMed
-
- Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Sugawara S, Oizumi S, Isobe H, et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:2380–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

